MiR-365: a mechanosensitive microRNA stimulates chondrocyte differentiation through targeting histone deacetylase 4
- PMID: 21856783
- PMCID: PMC3236620
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.11-185132
MiR-365: a mechanosensitive microRNA stimulates chondrocyte differentiation through targeting histone deacetylase 4
Abstract
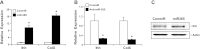
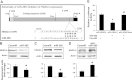
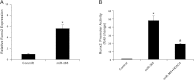
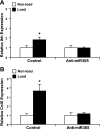
Mechanical stress plays an essential role in tissue development and remodeling. In this study, we determined the role of microRNA in chondrocyte mechanotransduction. Using microarray, we identified miR-365 as a mechanoresponsive microRNA in parallel to mechanical induction of Indian hedgehog (Ihh) in primary chicken chondrocytes cultured in 3-dimensional collagen scaffoldings under cyclic loading (1 Hz, 5% elongation). Interestingly, expression of miR-365 is elevated in the prehypertrophic zone of the growth plate, coinciding with the Ihh expression region in vivo. MiR-365 significantly stimulates chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. MiR-365 increases expression of Ihh and the hypertrophic marker type X collagen, whereas anti-miR-365 inhibits the expression of these genes. We identified histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4), an inhibitor of chondrocyte hypertrophy, as a target of miR-365. MiR-365 inhibits both endogenous HDAC4 protein levels as well as the activity of a reporter gene bearing the 3'-untranslated region of HDAC4 mRNA. Conversely, inhibition of endogenous miR-365 relieves the repression of HDAC4. Mutation of the miR-365 binding site in HDAC4 mRNA abolishes miR-365-mediated repression of the reporter gene activity. Overexpression of HDAC4 reverses miR-365 stimulation of chondrocyte differentiation markers including Ihh, Col X, and Runx2. Moreover, inhibition of miR-365 abolishes mechanical stimulation of chondrocyte differentiation. Taken together, miR-365 is the first identified mechanically responsive microRNA that regulates chondrocyte differentiation via directly targeting HDAC4.
Figures





References
-
- Bartel D. P. (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297 - PubMed
-
- Lewis B. P., Burge C. B., Bartel D. P. (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120, 15–20 - PubMed
-
- Chan S. P., Slack F. J. (2006) microRNA-mediated silencing inside P-bodies. RNA Biol. 3, 97–100 - PubMed
-
- Bushati N., Cohen S. M. (2007) microRNA functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 23, 175–205 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

