Altered hepatic lipid metabolism in C57BL/6 mice fed alcohol: a targeted lipidomic and gene expression study
- PMID: 21856784
- PMCID: PMC3196234
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M017368
Altered hepatic lipid metabolism in C57BL/6 mice fed alcohol: a targeted lipidomic and gene expression study
Abstract
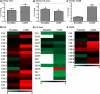
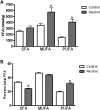
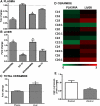
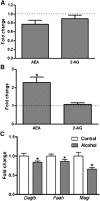
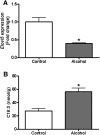
Chronic alcohol consumption is associated with fatty liver disease in mammals. The object of this study was to gain an understanding of dysregulated lipid metabolism in alcohol-fed C57BL/6 mice using a targeted lipidomic approach. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry was used to analyze several lipid classes, including free fatty acids, fatty acyl-CoAs, fatty acid ethyl esters, sphingolipids, ceramides, and endocannabinoids, in plasma and liver samples from control and alcohol-fed mice. The interpretation of lipidomic data was augmented by gene expression analyses for important metabolic enzymes in the lipid pathways studied. Alcohol feeding was associated with i) increased hepatic free fatty acid levels and decreased fatty acyl-CoA levels associated with decreased mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and decreased fatty acyl-CoA synthesis, respectively; ii) increased hepatic ceramide levels associated with higher levels of the precursor molecules sphingosine and sphinganine; and iii) increased hepatic levels of the endocannabinoid anandamide associated with decreased expression of its catabolic enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase. The unique combination of lipidomic and gene expression analyses allows for a better mechanistic understanding of dysregulated lipid metabolism in the development of alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Figures
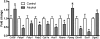
References
-
- Lakshman M. R. 2004. Some novel insights into the pathogenesis of alcoholic steatosis. Alcohol. 34: 45–48 - PubMed
-
- Sozio M. S., Liangpunsakul S., Crabb D. 2010. The role of lipid metabolism in the pathogenesis of alcoholic and nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 30: 378–390 - PubMed
-
- Oresic M. 2009. Metabolomics, a novel tool for studies of nutrition, metabolism and lipid dysfunction. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 19: 816–824 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

