G alpha i2 and ZAP-70 mediate RasGRP1 membrane localization and activation of SDF-1-induced T cell functions
- PMID: 21856938
- PMCID: PMC3169754
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100206
G alpha i2 and ZAP-70 mediate RasGRP1 membrane localization and activation of SDF-1-induced T cell functions
Abstract
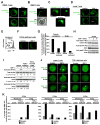
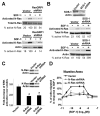
RasGRP1, a Ras guanine-nucleotide exchange factor, critically mediates T cell development and function and controls immunodeficiency and autoimmunity. In this study, we describe a unique mechanism of mobilization and activation of RasGRP1 in response to SDF-1, a chemokine that signals via the G protein-coupled receptor CXCR4. Depletion of RasGRP1 impaired SDF-1-stimulated human T cell migration, expression of the activation marker CD69, and activation of the ERK MAPK pathway, indicating that RasGRP1 mediates SDF-1 functions. SDF-1 treatment caused RasGRP1 to localize to the plasma membrane to activate K-Ras and to the Golgi to activate N-Ras. These events were required for cellular migration and for ERK activation that mediates downstream transcriptional events in response to SDF-1. SDF-1-dependent localization of RasGRP1 did not require its diacylglycerol-binding domain, even though diacyglycerol was previously shown to mediate localization of RasGRP1 in response to Ag stimulation. This domain was, however, required for activity of RasGRP1 after its localization. Intriguingly, SDF-1 treatment of T cells induced the formation of a novel molecular signaling complex containing RasGRP1, Gαi2, and ZAP-70. Moreover, SDF-1-mediated signaling by both Gi proteins and ZAP-70 was required for RasGRP1 mobilization. In addition, RasGRP1 mobilization and activation in response to SDF-1 was dependent on TCR expression, suggesting that CXCR4 heterodimerizes with the TCR to couple to ZAP-70 and mobilize RasGRP1. These results increase understanding of the molecular mechanisms that mediate SDF-1 effects on T cells and reveal a novel mechanism of RasGRP1 regulation. Other G protein-coupled receptors may similarly contribute to regulation of RasGRP1.
Figures




References
-
- Suzuki Y, Rahman M, Mitsuya H. Diverse transcriptional response of CD4(+) T cells to stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1: cell survival promotion and priming effects of SDF-1 on CD4(+) T cells. J Immunol. 2001;167:3064–3073. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Humphreys TD, Kremer KN, Bramati PS, Bradfield L, Edgar CE, Hedin KE. CXCR4 physically associates with the T cell receptor to signal in T cells. Immunity. 2006;25:213–224. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

