In vivo and in vitro tracking of erosion in biodegradable materials using non-invasive fluorescence imaging
- PMID: 21857678
- PMCID: PMC3160718
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat3095
In vivo and in vitro tracking of erosion in biodegradable materials using non-invasive fluorescence imaging
Erratum in
- Nat Mater. 2011 Nov;10(11):896
Abstract
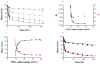
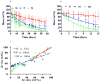
The design of erodible biomaterials relies on the ability to program the in vivo retention time, which necessitates real-time monitoring of erosion. However, in vivo performance cannot always be predicted by traditional determination of in vitro erosion, and standard methods sacrifice samples or animals, preventing sequential measures of the same specimen. We harnessed non-invasive fluorescence imaging to sequentially follow in vivo material-mass loss to model the degradation of materials hydrolytically (PEG:dextran hydrogel) and enzymatically (collagen). Hydrogel erosion rates in vivo and in vitro correlated, enabling the prediction of in vivo erosion of new material formulations from in vitro data. Collagen in vivo erosion was used to infer physiologic in vitro conditions that mimic erosive in vivo environments. This approach enables rapid in vitro screening of materials, and can be extended to simultaneously determine drug release and material erosion from a drug-eluting scaffold, or cell viability and material fate in tissue-engineering formulations.
Figures


References
-
- Grayson AC, et al. Differential degradation rates in vivo and in vitro of biocompatible poly(lactic acid) and poly(glycolic acid) homo- and co-polymers for a polymeric drug-delivery microchip. Journal of biomaterials science. 2004;15:1281–1304. - PubMed
-
- Benny O, et al. In vivo fate and therapeutic efficacy of PF-4/CTF microspheres in an orthotopic human glioblastoma model. Faseb J. 2008;22:488–499. - PubMed
-
- Gopferich A. Mechanisms of polymer degradation and erosion. Biomaterials. 1996;17:103–114. - PubMed
-
- Anseth KS, Shastri VR, Langer R. Photopolymerizable degradable polyanhydrides with osteocompatibility. Nature biotechnology. 1999;17:156–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

