Inferring a transcriptional regulatory network from gene expression data using nonlinear manifold embedding
- PMID: 21857910
- PMCID: PMC3155518
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021969
Inferring a transcriptional regulatory network from gene expression data using nonlinear manifold embedding
Abstract
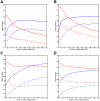
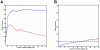
Transcriptional networks consist of multiple regulatory layers corresponding to the activity of global regulators, specialized repressors and activators as well as proteins and enzymes shaping the DNA template. Such intrinsic complexity makes uncovering connections difficult and it calls for corresponding methodologies, which are adapted to the available data. Here we present a new computational method that predicts interactions between transcription factors and target genes using compendia of microarray gene expression data and documented interactions between genes and transcription factors. The proposed method, called Kernel Embedding of Regulatory Networks (KEREN), is based on the concept of gene-regulon association, and captures hidden geometric patterns of the network via manifold embedding. We applied KEREN to reconstruct transcription regulatory interactions on a genome-wide scale in the model bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli). Application of the method not only yielded accurate predictions of verifiable interactions, which outperformed on certain metrics comparable methodologies, but also demonstrated the utility of a geometric approach in the analysis of high-dimensional biological data. We also described possible applications of kernel embedding techniques to other function and network discovery algorithms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reconstruction of Escherichia coli transcriptional regulatory networks via regulon-based associations.BMC Syst Biol. 2009 Apr 14;3:39. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-3-39. BMC Syst Biol. 2009. PMID: 19366454 Free PMC article.
-
MICRAT: a novel algorithm for inferring gene regulatory networks using time series gene expression data.BMC Syst Biol. 2018 Dec 14;12(Suppl 7):115. doi: 10.1186/s12918-018-0635-1. BMC Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 30547796 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Approaches for Inference of Genome-Scale Gene Regulatory Networks.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1883:161-194. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8882-2_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30547400
-
Inferring regulatory networks.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:263-75. doi: 10.2741/2677. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981545 Review.
-
Computational and experimental approaches for modeling gene regulatory networks.Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(14):1415-36. doi: 10.2174/138161207780765945. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17504165 Review.
Cited by
-
From ERα66 to ERα36: a generic method for validating a prognosis marker of breast tumor progression.BMC Syst Biol. 2015 Jun 17;9:28. doi: 10.1186/s12918-015-0178-7. BMC Syst Biol. 2015. PMID: 26080803 Free PMC article.
-
Multiview learning for understanding functional multiomics.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Apr 2;16(4):e1007677. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007677. eCollection 2020 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32240163 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Friedman N, Linial M, Nachman I, Pe'er D. Using Bayesian networks to analyze expression data. J Comput Biol. 2000;7:601–620. - PubMed
-
- Perrin BE, Ralaivola L, Mazurie A, Bottani S, Mallet J, et al. Gene networks inference using dynamic Bayesian networks. Bioinformatics. 2003;19(2):38–48. - PubMed
-
- Kim S, Imoto S, Miyano S. Dynamic Bayesian network and nonparametric regression for nonlinear modeling of gene networks from time series gene expression data. Biosystems. 2004;75(1–3):57–65. - PubMed
-
- Butte AJ, Kohane IS. Mutual information relevance networks: Functional genomic clustering using pairwise entropy measurements. Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing. 2002:418–429. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

