Systematic targeted integration to study Albumin gene control elements
- PMID: 21858039
- PMCID: PMC3155544
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023234
Systematic targeted integration to study Albumin gene control elements
Abstract
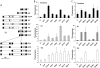
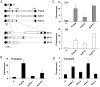
To study transcriptional regulation by distant enhancers, we devised a system of easily modified reporter plasmids for integration into single-copy targeting cassettes in clones of HuH7, a human hepatocellular carcinoma. The plasmid constructs tested transcriptional function of a 35-kb region that contained the rat albumin gene and its upstream flanking region. Expression of integrants was analyzed in two orientations, and compared to transient expression of non-integrated plasmids. Enhancers were studied in their natural positions relative to the promoter and localized by deletion. All constructs were also analyzed by transient transfection assays. In addition to the known albumin gene enhancer (E1 at -10 kb), we demonstrated two new enhancers, E2 at -13, and E4 at +1.2 kb. All three enhancers functioned in both transient assays and integrated constructs. However, chromosomal integration demonstrated several differences from transient expression. For example, analysis of E2 showed that enhancer function within the chromosome required a larger gene region than in transient assays. Another conserved region, E3 at -0.7 kb, functioned as an enhancer in transient assays but inhibited the function of E1 and E2 when chromosomally integrated. The enhancers did not show additive or synergistic behavior,an effect consistent with competition for the promoter or inhibitory interactions among enhancers. Growth arrest by serum starvation strongly stimulated the function of some integrated enhancers, consistent with the expected disruption of enhancer-promoter looping during the cell cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Buttgereit D. Redundant enhancer elements guide beta 1 tubulin gene expression in apodemes during Drosophila embryogenesis. J Cell Sci. 1993;105:721–727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

