Synaptic connections of the neurokinin 1 receptor-like immunoreactive neurons in the rat medullary dorsal horn
- PMID: 21858052
- PMCID: PMC3157358
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023275
Synaptic connections of the neurokinin 1 receptor-like immunoreactive neurons in the rat medullary dorsal horn
Abstract
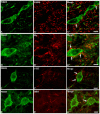
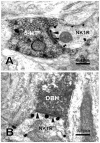
The synaptic connections between neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor-like immunoreactive (LI) neurons and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-, glycine (Gly)-, serotonin (5-HT)- or dopamine-β-hydroxylase (DBH, a specific marker for norepinephrinergic neuronal structures)-LI axon terminals in the rat medullary dorsal horn (MDH) were examined under electron microscope by using a pre-embedding immunohistochemical double-staining technique. NK1 receptor-LI neurons were observed principally in laminae I and III, only a few of them were found in lamina II of the MDH. GABA-, Gly-, 5-HT-, or DBH-LI axon terminals were densely encountered in laminae I and II, and sparsely in lamina III of the MDH. Some of these GABA-, Gly-, 5-HT-, or DBH-LI axon terminals were observed to make principally symmetric synapses with NK1 receptor-LI neuronal cell bodies and dendritic processes in laminae I, II and III of the MDH. The present results suggest that neurons expressing NK1 receptor within the MDH might be modulated by GABAergic and glycinergic inhibitory intrinsic neurons located in the MDH and 5-HT- or norepinephrine (NE)-containing descending fibers originated from structures in the brainstem.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synaptic connections between trigemino-parabrachial projection neurons and gamma-aminobutyric acid- and glycine-immunoreactive terminals in the rat.Brain Res. 2001 Dec 7;921(1-2):133-7. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)03109-2. Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11720719
-
gamma-aminobutyric acid- and glycine-immunoreactive neurons postsynaptic to substance P-immunoreactive axon terminals in the superficial layers of the rat medullary dorsal horn.Neurosci Lett. 2000 Jul 21;288(3):187-90. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(00)01226-x. Neurosci Lett. 2000. PMID: 10889339
-
Differential contribution of GABAergic and glycinergic components to inhibitory synaptic transmission in lamina II and laminae III-IV of the young rat spinal cord.Eur J Neurosci. 2007 Nov;26(10):2940-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05919.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 18001289
-
GABAergic and glycinergic synapses onto neurokinin-1 receptor-immunoreactive neurons in the pre-Bötzinger complex of rats: light and electron microscopic studies.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Sep;16(6):1058-66. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02163.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12383234
-
Anatomy of primary afferents and projection neurones in the rat spinal dorsal horn with particular emphasis on substance P and the neurokinin 1 receptor.Exp Physiol. 2002 Mar;87(2):245-9. doi: 10.1113/eph8702351. Exp Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11856970 Review.
References
-
- Willis WD, Westlund KN, Carlton SM. The rat nervous system. In: Paxinos G, editor. Pain. San Diego: Academic Press; 1995. pp. 725–750.
-
- Li YQ, Li H, Kaneko T, Mizuno N. Substantia gelatinosa neurons in the medullary dorsal horn: An intracellular labeling study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1999;411:399–412. - PubMed
-
- Li YQ, Li H, Yang K, Kaneko T, Mizuno N. Morphologic features and electrical membrane properties of projection neurons in the marginal layer of the medullary dorsal horn of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 2000;424:24–36. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Bao L. The development and modulation of nociceptive circuitry. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006;16:460–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

