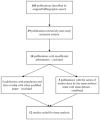
Widowhood and mortality: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 21858130
- PMCID: PMC3157386
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023465
Widowhood and mortality: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: While the "widowhood effect" is well known, there is substantial heterogeneity in the magnitude of effects reported in different studies. We conducted a meta-analysis of widowhood and mortality, focusing on longitudinal studies with follow-up from the time of bereavement.
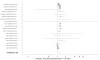
Methods and findings: A random-effects meta-analysis was conducted to calculate the overall relative risk (RR) for subsequent mortality among 2,263,888 subjects from 15 prospective cohort studies. We found a statistically significant positive association between widowhood and mortality, but the widowhood effect was stronger in the period earlier than six months since bereavement (overall RR = 1.41, 95% CI: 1.26, 1.57) compared to the effect after six months (overall RR = 1.14, 95% CI: 1.10, 1.18). Meta-regression showed that the widowhood effect was not different for those aged younger than 65 years compared to those older than 65 (P = 0.25). There was, however, a difference in the magnitude of the widowhood effect by gender; for women the RR was not statistically significantly different from the null (overall RR = 1.04, 95% CI: 1.00, 1.08), while it was for men (overall RR = 1.23, 95% CI: 1.18, 1.28).
Conclusions: The results suggest that further studies should focus more on the mechanisms that generate this association especially among men.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Hu YR, Goldman N. Mortality differentials by marital status: an international comparison. Demography. 1990;27:233–250. - PubMed
-
- Helsing KJ, Comstock GW, Szklo M. Causes of death in a widowed population. Am J Epidemiol. 1982;116:524–532. - PubMed
-
- Lillard LA, Waite LJ. 'Til Death Do Us Part: Marital Disruption and Mortality. American Journal of Sociology. 1995;1001131-1156
-
- Krause AS, Lilienfeld AM. Some epidemiologic aspects of the high mortality rate in the young widowed group. J Chronic Dis. 1959;10:207–217. - PubMed