Isolation of genes involved in biofilm formation of a Klebsiella pneumoniae strain causing pyogenic liver abscess
- PMID: 21858144
- PMCID: PMC3155550
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023500
Isolation of genes involved in biofilm formation of a Klebsiella pneumoniae strain causing pyogenic liver abscess
Abstract
Background: Community-acquired pyogenic liver abscess (PLA) complicated with meningitis and endophthalmitis caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae is an emerging infectious disease. To investigate the mechanisms and effects of biofilm formation of K. pneumoniae causing PLA, microtiter plate assays were used to determine the levels of biofilm formed by K. pneumoniae clinical isolates and to screen for biofilm-altered mutants from a transposon mutant library of a K. pneumoniae PLA-associated strain.
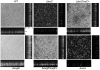
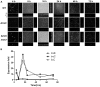
Methodology/principal findings: The biofilm formation of K. pneumoniae was examined by microtiter plate assay. Higher levels of biofilm formation were demonstrated by K. pneumoniae strains associated with PLA. A total of 23 biofilm-decreased mutants and 4 biofilm-increased mutants were identified. Among these mutants, a biofilm-decreased treC mutant displayed less mucoviscosity and produced less capsular polysaccharide (CPS), whereas a biofilm-increased sugE mutant displayed higher mucoviscosity and produced more CPS. The biofilm phenotypes of treC and sugE mutants also were confirmed by glass slide culture. Deletion of treC, which encodes trehalose-6-phosphate hydrolase, impaired bacterial trehalose utilization. Addition of glucose to the culture medium restored the capsule production and biofilm formation in the treC mutant. Transcriptional profile analysis suggested that the increase of CPS production in ΔsugE may reflect elevated cps gene expression (upregulated through rmpA) in combination with increased treC expression. In vivo competition assays demonstrated that the treC mutant strain was attenuated in competitiveness during intragastric infection in mice.
Conclusions/significance: Genes important for biofilm formation by K. pneumoniae PLA strain were identified using an in vitro assay. Among the identified genes, treC and sugE affect biofilm formation by modulating CPS production. The importance of treC in gastrointestinal tract colonization suggests that biofilm formation contributes to the establishment and persistence of K. pneumoniae infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
Lipopolysaccharide O1 antigen contributes to the virulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae causing pyogenic liver abscess.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033155. Epub 2012 Mar 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22427976 Free PMC article.
-
Cellobiose-specific phosphotransferase system of Klebsiella pneumoniae and its importance in biofilm formation and virulence.Infect Immun. 2012 Jul;80(7):2464-72. doi: 10.1128/IAI.06247-11. Epub 2012 May 7. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22566508 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of cAMP receptor protein in biofilm formation, fimbria production, capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis and lethality in mouse of Klebsiella pneumoniae serotype K1 causing pyogenic liver abscess.J Med Microbiol. 2017 Jan;66(1):1-7. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000391. Epub 2017 Feb 6. J Med Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27902401
-
Pyogenic liver abscess complicated with endogenous endophthalmitis caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae: A case report and Literature Review.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Jul;11(7):e943. doi: 10.1002/iid3.943. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37506152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Klebsiella pneumoniae genotype K1: an emerging pathogen that causes septic ocular or central nervous system complications from pyogenic liver abscess.Clin Infect Dis. 2007 Aug 1;45(3):284-93. doi: 10.1086/519262. Epub 2007 Jun 19. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17599305 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of the genes involved in Riemerella anatipestifer biofilm formation by random transposon mutagenesis.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039805. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768127 Free PMC article.
-
Pasteurella multocida: Genotypes and Genomics.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2019 Sep 4;83(4):e00014-19. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00014-19. Print 2019 Nov 20. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31484691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial Activity study of Musizin isolated from Rhamnus wightii Wight and Arn.Bioinformation. 2018 Dec 21;14(9):511-520. doi: 10.6026/97320630014511. eCollection 2018. Bioinformation. 2018. PMID: 31223211 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular Protective Functions and Therapeutical Potential of Trehalose.Molecules. 2024 May 1;29(9):2088. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092088. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
iTRAQ-Based Proteomics Reveals Potential Anti-Virulence Targets for ESBL-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae.Infect Drug Resist. 2020 Aug 19;13:2891-2899. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S259894. eCollection 2020. Infect Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 32903891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ramphal R, Ambrose PG. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases and clinical outcomes: current data. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42(Suppl 4):S164–172. - PubMed
-
- Chang SC, Fang CT, Hsueh PR, Chen YC, Luh KT. Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates causing liver abscess in Taiwan. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000;37:279–284. - PubMed
-
- Chuang YP, Fang CT, Lai SY, Chang SC, Wang JT. Genetic determinants of capsular serotype K1 of Klebsiella pneumoniae causing primary pyogenic liver abscess. J Infect Dis. 2006;193:645–654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

