Activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) leads to reciprocal epigenetic regulation of FoxP3 and IL-17 expression and amelioration of experimental colitis
- PMID: 21858153
- PMCID: PMC3156147
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023522
Activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) leads to reciprocal epigenetic regulation of FoxP3 and IL-17 expression and amelioration of experimental colitis
Abstract
Background: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), a transcription factor of the bHLH/PAS family, is well characterized to regulate the biochemical and toxic effects of environmental chemicals. More recently, AhR activation has been shown to regulate the differentiation of Foxp3(+) Tregs as well as Th17 cells. However, the precise mechanisms are unclear. In the current study, we investigated the effect of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), a potent AhR ligand, on epigenetic regulation leading to altered Treg/Th17 differentiation, and consequent suppression of colitis.
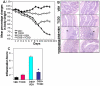
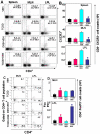
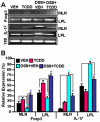
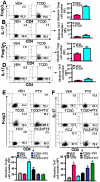
Methodology/principal findings: Dextran sodium sulphate (DSS) administration induced acute colitis in C57BL/6 mice, as shown by significant weight loss, shortening of colon, mucosal ulceration, and increased presence of CXCR3(+) T cells as well as inflammatory cytokines. Interestingly, a single dose of TCDD (25 µg/kg body weight) was able to attenuate all of the clinical and inflammatory markers of colitis. Analysis of T cells in the lamina propria (LP) and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN), during colitis, revealed decreased presence of Tregs and increased induction of Th17 cells, which was reversed following TCDD treatment. Activation of T cells from AhR(+/+) but not AhR (-/-) mice, in the presence of TCDD, promoted increased differentiation of Tregs while inhibiting Th17 cells. Analysis of MLN or LP cells during colitis revealed increased methylation of CpG islands of Foxp3 and demethylation of IL-17 promoters, which was reversed following TCDD treatment.
Conclusions/significance: These studies demonstrate for the first time that AhR activation promotes epigenetic regulation thereby influencing reciprocal differentiation of Tregs and Th17 cells, and amelioration of inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Tian Y. Ah receptor and NF-kappaB interplay on the stage of epigenome. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77:670–680. - PubMed
-
- Hahn ME. Aryl hydrocarbon receptors: diversity and evolution. Chem Biol Interact. 2002;141:131–160. - PubMed
-
- Hu W, Sorrentino C, Denison MS, Kolaja K, Fielden MR. Induction of cyp1a1 is a nonspecific biomarker of aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation: results of large scale screening of pharmaceuticals and toxicants in vivo and in vitro. Molecular Pharmacology. 2007;71:1475–1486. - PubMed
-
- Bock KW, Kohle C. Ah receptor: dioxin-mediated toxic responses as hints to deregulated physiologic functions. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72:393–404. - PubMed
-
- Esser C, Rannug A, Stockinger B. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor in immunity. Trends in Immunology. 2009;30:447–454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

