A higher correlation of HCV core antigen with CD4+ T cell counts compared with HCV RNA in HCV/HIV-1 coinfected patients
- PMID: 21858166
- PMCID: PMC3155566
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023550
A higher correlation of HCV core antigen with CD4+ T cell counts compared with HCV RNA in HCV/HIV-1 coinfected patients
Abstract
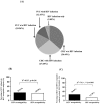
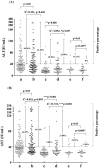
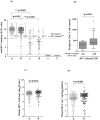
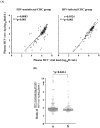
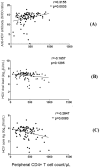
Development of HCV infection is typically followed by chronic hepatitis C (CHC) in most patients, while spontaneous HCV viral clearance (SVC) occurs in only a minority of subjects. Compared with the widespread application of HCV RNA testing by quantitative RT-PCR technique, HCV core antigen detection may be an alternative indicator in the diagnosis of hepatitis C virus infections and in monitoring the status of infectious individuals. However, the correlation and differences between these two indicators in HCV infection need more investigation, especially in patients coinfected by HIV-1. In this study, a total of 354 anti-HCV and/or anti-HIV serum positive residents from a village of central China were enrolled. Besides HCV-related hepatopathic variables including clinical status, ALT, AST, anti-HCV Abs, as well as the altered CD4+/CD8+ T cell counts, HCV core antigen and HCV viral load were also measured. The concentration of serum HCV core antigen was highly correlated with level of HCV RNA in CHC patients with or without HIV-1 coinfection. Of note, HCV core antigen concentration was negatively correlated with CD4+ T cell count, while no correlation was found between HCV RNA level and CD4+ T cell count. Our findings suggested that quantitative detection of plasma HCV core antigen may be an alternative indicator of HCV RNA qPCR assay when evaluating the association between HCV replication and host immune status in HCV/HIV-1 coinfected patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of HCV core antigen and RNA quantification in HCV-infected and HCV/HIV-1-coinfected patients.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Nov 5;14:577. doi: 10.1186/s12879-014-0577-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25371245 Free PMC article.
-
HCV-specific T-cell responses in HIV/hepatitis C virus-coinfected patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy are comparable to those observed in hepatitis C virus-monoinfected individuals.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011 May 1;57(1):1-8. doi: 10.1097/qai.0b013e31821024e7. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2011. PMID: 21786458
-
Effect of coexisting HIV-1 infection on the diagnosis and evaluation of hepatitis C virus.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2001 Apr 1;26(4):340-4. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200104010-00008. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2001. PMID: 11317075
-
Hepatitis C virus core antigen testing: role in diagnosis, disease monitoring and treatment.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun 14;20(22):6701-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.6701. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24944462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HCV core antigen plays an important role in the fight against HCV as an alternative to HCV-RNA detection.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Jun;35(6):e23755. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23755. Epub 2021 Mar 31. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33788295 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polymorphisms in the Th17 cell-related RORC gene are associated with spontaneous clearance of HCV in Chinese women.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Jun 4;18(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3153-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29866105 Free PMC article.
-
HCV core antigen and HCV-RNA in HIV/HCV co-infected patients with different HCV genotypes.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Apr 23;14:222. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-222. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24758157 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of HCV core antigen and RNA quantification in HCV-infected and HCV/HIV-1-coinfected patients.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Nov 5;14:577. doi: 10.1186/s12879-014-0577-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25371245 Free PMC article.
-
HIV co-infection accelerates decay of humoral responses in spontaneous resolvers of HCV infection.J Viral Hepat. 2014 Oct;21(10):690-5. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12238. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Viral Hepat. 2014. PMID: 24861885 Free PMC article.
-
Liver Damage in Patients with HCV/HIV Coinfection Is Linked to HIV-Related Oxidative Stress.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:8142431. doi: 10.1155/2016/8142431. Epub 2016 Jan 10. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 26881041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu Z, Liu Z, Detels R. HIV-1 infection in commercial plasma donors in China. Lancet. 1995;346:61–62. - PubMed
-
- Wu Z, Rou K, Detels R. Prevalence of HIV infection among former commercial plasma donors in rural eastern China. Health Policy Plan. 2001;16:41–46. - PubMed
-
- Thomas DL, Zenilman JM, Alter HJ, Shih JW, Galai N, et al. Sexual transmission of hepatitis C virus among patients attending sexually transmitted diseases clinics in Baltimore--an analysis of 309 sex partnerships. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:768–775. - PubMed
-
- Thomas DL. Hepatitis C and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Hepatology. 2002;36:S201–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

