The neuromuscular activity of Micrurus pyrrhocryptus venom and its neutralization by commercial and specific coral snake antivenoms
- PMID: 21858249
- PMCID: PMC3132105
The neuromuscular activity of Micrurus pyrrhocryptus venom and its neutralization by commercial and specific coral snake antivenoms
Abstract
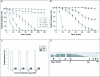
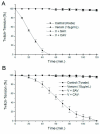
The neuromuscular activity ofMicrurus pyrrochryptus venom was studied in chick biventer cervicis (BC) and mouse phrenic nerve-diaphragm (PND) preparations. The venom (0.5-50μg/ml) caused irreversible, time- and concentration-dependent blockade, with BC being more sensitive than PND (50% blockade with 10μg/ml in 22±;3min and 62±4min, respectively; mean±SEM, n=6; p<0.05). In BC preparations, venom (0.5μg/ml) progressively abolished ACh-induced contractures, whereas contractures to exogenous KCl and muscle twitches in curarized preparations were unaffected. The venom neither altered creatine kinase release (venom: 25.8±1.75IU/l vs control: 24.3±2.2IU/l, n=6, after 120min), nor it caused significant muscle damage (50μg of venom/ml vs control: 3.5±0.8% vs 1.1±0.7% for PND; 4.3±1.5% vs 1.2±0.5% for BC, n=5). The venom had low PLA(2) activity. Neurotoxicity was effectively neutralized by commercial Micrurus antivenom and specific antivenom. These findings indicate that M. pyrrhocryptus venom acts postsynaptically on nicotinic receptors, with no significant myotoxicity.
Keywords: Coral snake venom; neuromuscular blockade; neurotoxin; nicotinic receptor; postsynaptic.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neurotoxicity of Micrurus lemniscatus lemniscatus (South American coralsnake) venom in vertebrate neuromuscular preparations in vitro and neutralization by antivenom.Arch Toxicol. 2019 Jul;93(7):2065-2086. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02476-9. Epub 2019 May 23. Arch Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31123802
-
Neuromuscular activity of Bothrops fonsecai snake venom in vertebrate preparations.J Venom Res. 2014 Jun 18;5:6-15. eCollection 2014. J Venom Res. 2014. PMID: 25028603 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotoxicity of Micrurus altirostris (Uruguayan coral snake) venom and its neutralization by commercial coral snake antivenom and specific antiserum raised in rabbits.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2008 Jul;46(6):519-27. doi: 10.1080/15563650701647405. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2008. PMID: 18584364
-
Biological activities of Leptodeira annulata (banded cat-eyed snake) venom on vertebrate neuromuscular preparations.Toxicon. 2016 Sep 1;119:345-51. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Toxicon. 2016. PMID: 27390040
-
Coral snake bites (Micrurus spp.) in Brazil: a review of literature reports.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016 Mar;54(3):222-34. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2015.1135337. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016. PMID: 26808120 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunogenic potential and neutralizing ability of a heterologous version of the most abundant three-finger toxin from the coral snake Micrurus mipartitus.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2024 Nov 25;30:e20230074. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2023-0074. eCollection 2024. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39628669 Free PMC article.
-
The Bold and the Beautiful: a Neurotoxicity Comparison of New World Coral Snakes in the Micruroides and Micrurus Genera and Relative Neutralization by Antivenom.Neurotox Res. 2017 Oct;32(3):487-495. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9771-4. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Neurotox Res. 2017. PMID: 28674788
-
In Vitro Tests for Assessing the Neutralizing Ability of Snake Antivenoms: Toward the 3Rs Principles.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 11;11:617429. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.617429. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33505403 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromuscular activity of Micrurus laticollaris (Squamata: Elapidae) venom in vitro.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Jan 17;6(1):359-70. doi: 10.3390/toxins6010359. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24445448 Free PMC article.
-
From squid giant axon to automated patch-clamp: electrophysiology in venom and antivenom research.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 24;14:1249336. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1249336. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37693897 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abreu VA, Leite GB, Oliveira CB, Hyslop S, Furtado MF, Rodrigues-Simioni L. Neurotoxicity of Micrurus altirostris (Uruguayan coral snake) venom and its neutralization by commercial coral snake antivenom and specific antiserum raised in rabbits. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 2008;46:519–527. - PubMed
-
- Aird SD, da Silva NJ., Jr Comparative enzymatic composition of Brazilian coral snake (Micrurus) venoms. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1991;99B:287–294. - PubMed
-
- Alape-Girón A, Miranda-Arrieta K, Cortes-Bratti X, Stiles BG, Gutiérrez JM. A comparison of in vitro methods for assessing the potency of therapeutic antisera against the venom of the coral snake Micrurus nigrocinctus. Toxicon. 1997;35:573–581. - PubMed
-
- Alapé-Girón A, Stiles BG, Gutiérrez JM. Antibody-mediated neutralization and binding-reversal studies on α-neurotoxins from Micrurus nigrocinctus nigrocinctus (coral snake) venom. Toxicon. 1996a;34:369–380. - PubMed
-
- Alapé-Girón A, Stiles B, Schmidt J, Girón-Cortes M, Thelestam M, Hörnvall H, Bergman T. Characterization of multiple nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-binding proteins and phospholipases A2 from the venom of the coral snake Micrurus nigrocinctus nigrocinctus. FEBS Lett. 1996b;380:29–32. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
