A systematic review of adherence to cardiovascular medications in resource-limited settings
- PMID: 21858602
- PMCID: PMC3235604
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-011-1825-3
A systematic review of adherence to cardiovascular medications in resource-limited settings
Abstract
Background: Medications are a cornerstone of the prevention and management of cardiovascular disease. Long-term medication adherence has been the subject of increasing attention in the developed world but has received little attention in resource-limited settings, where the burden of disease is particularly high and growing rapidly. To evaluate prevalence and predictors of non-adherence to cardiovascular medications in this context, we systematically reviewed the peer-reviewed literature.
Methods: We performed an electronic search of Ovid Medline, Embase and International Pharmaceutical Abstracts from 1966 to August 2010 for studies that measured adherence to cardiovascular medications in the developing world. A DerSimonian-Laird random effects method was used to pool the adherence estimates across studies. Between-study heterogeneity was estimated with an I(2) statistic and studies were stratified by disease group and the method by which adherence was assessed. Predictors of non-adherence were also examined.
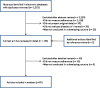
Findings: Our search identified 2,353 abstracts, of which 76 studies met our inclusion criteria. Overall adherence was 57.5% (95% confidence interval [CI] 52.3% to 62.7%; I(2) 0.98) and was consistent across study subgroups. Studies that assessed adherence with pill counts reported higher levels of adherence (62.1%, 95% CI 49.7% to 73.8%; I(2) 0.83) than those using self-report (54.6%, 95% CI 47.7% to 61.5%; I(2) 0.93). Adherence did not vary by geographic region, urban vs. rural settings, or the complexity of a patient's medication regimen. The most common predictors of poor adherence included poor knowledge, negative perceptions about medication, side effects and high medication costs.
Interpretation: Our study indicates that adherence to cardiovascular medication in resource-limited countries is sub-optimal and appears very similar to that observed in resource-rich countries. Efforts to improve adherence in resource-limited settings should be a priority given the burden of heart disease in this context, the central role of medications in their management, and the clinical and economic consequences of non-adherence.
Figures



Comment in
-
The importance of social ties in sustaining medication adherence in resource-limited settings.J Gen Intern Med. 2011 Dec;26(12):1391-3. doi: 10.1007/s11606-011-1841-3. J Gen Intern Med. 2011. PMID: 21879369 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO. Adherence to Long-term Therapies: Evidence for action. World Health Organisation 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

