BMP-2 gene-fibronectin-apatite composite layer enhances bone formation
- PMID: 21859498
- PMCID: PMC3175450
- DOI: 10.1186/1423-0127-18-62
BMP-2 gene-fibronectin-apatite composite layer enhances bone formation
Abstract
Background: Safe and efficient gene transfer systems are needed for tissue engineering. We have developed an apatite composite layer including the bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) gene and fibronectin (FB), and we evaluated its ability to induce bone formation.
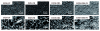
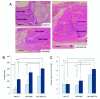
Methods: An apatite composite layer was evaluated to determine the efficiency of gene transfer to cells cultured on it. Cells were cultured on a composite layer including the BMP-2 gene and FB, and BMP-2 gene expression, BMP-2 protein concentrations, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, and osteocalcin (OC) concentrations were measured. A bone defect on the cranium of rats was treated with hydroxyapatite (HAP)-coated ceramic buttons with the apatite composite layer including the BMP-2 gene and FB (HAP-BMP-FB). The tissue concentration of BMP-2, bone formation, and the expression levels of the BMP-2, ALP, and OC genes were all quantified.
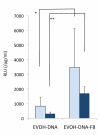
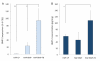
Results: The apatite composite layer provided more efficient gene transfer for the cultured cells than an apatite composite layer without FB. The BMP-2 concentration was approximately 100-600 pg/mL in the cell-culture medium. Culturing the cells on the apatite composite layer for 27 days increased ALP activity and OC concentrations. In animal experiments, the tissue concentrations of BMP-2 were over 100 pg/mg in the HAP-BMP-FB group and approximately 50 pg/mg in the control groups. Eight weeks later, bone formation was more enhanced in the HAP-BMP-FB group than in the control groups. In the tissues surrounding the HAP button, the gene expression levels of ALP and OC increased.
Conclusion: The BMP-2 gene-FB-apatite composite layer might be useful for bone engineering.
Figures


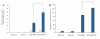
References
-
- Baltzer AW, Lattermann C, Whalen JD, Wooley P, Weiss K, Grimm M, Ghivizzani SC, Robbins PD, Evans CH. Genetic enhancement of fracture repair: healing of an experimental segmental defect by adenoviral transfer of the BMP-2 gene. Gene Ther. 2000;7:734–739. - PubMed
-
- Lieberman JR, Daluiski A, Stevenson S, Wu L, McAllister P, Lee YP, Kabo JM, Finerman GA, Berk AJ, Witte ON. The effect of regional gene therapy with bone morphogenetic protein-2-producing bone-marrow cells on the repair of segmental femoral defects in rats. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 1999;81:905–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

