Extracellular ATP acts on P2Y2 purinergic receptors to facilitate HIV-1 infection
- PMID: 21859844
- PMCID: PMC3171090
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20101805
Extracellular ATP acts on P2Y2 purinergic receptors to facilitate HIV-1 infection
Abstract
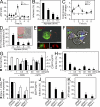
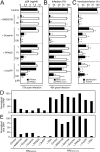
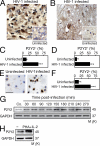
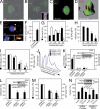
Extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) can activate purinergic receptors of the plasma membrane and modulate multiple cellular functions. We report that ATP is released from HIV-1 target cells through pannexin-1 channels upon interaction between the HIV-1 envelope protein and specific target cell receptors. Extracellular ATP then acts on purinergic receptors, including P2Y2, to activate proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2) kinase and transient plasma membrane depolarization, which in turn stimulate fusion between Env-expressing membranes and membranes containing CD4 plus appropriate chemokine co-receptors. Inhibition of any of the constituents of this cascade (pannexin-1, ATP, P2Y2, and Pyk2) impairs the replication of HIV-1 mutant viruses that are resistant to conventional antiretroviral agents. Altogether, our results reveal a novel signaling pathway involved in the early steps of HIV-1 infection that may be targeted with new therapeutic approaches.
© 2011 Séror et al.
Figures


References
-
- Abbracchio M.P., Boeynaems J.M., Barnard E.A., Boyer J.L., Kennedy C., Miras-Portugal M.T., King B.F., Gachet C., Jacobson K.A., Weisman G.A., Burnstock G. 2003. Characterization of the UDP-glucose receptor (re-named here the P2Y14 receptor) adds diversity to the P2Y receptor family. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 24:52–55 10.1016/S0165-6147(02)00038-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abbracchio M.P., Burnstock G., Boeynaems J.M., Barnard E.A., Boyer J.L., Kennedy C., Knight G.E., Fumagalli M., Gachet C., Jacobson K.A., Weisman G.A. 2006. International Union of Pharmacology LVIII: update on the P2Y G protein-coupled nucleotide receptors: from molecular mechanisms and pathophysiology to therapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 58:281–341 10.1124/pr.58.3.3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bacheler L.T., Anton E.D., Kudish P., Baker D., Bunville J., Krakowski K., Bolling L., Aujay M., Wang X.V., Ellis D., et al. 2000. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutations selected in patients failing efavirenz combination therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44:2475–2484 10.1128/AAC.44.9.2475-2484.2000 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

