Structural resolution of the complex between a fungal polygalacturonase and a plant polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein by small-angle X-ray scattering
- PMID: 21859985
- PMCID: PMC3192570
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.111.181057
Structural resolution of the complex between a fungal polygalacturonase and a plant polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein by small-angle X-ray scattering
Abstract
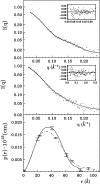
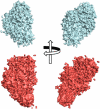
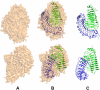
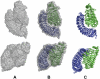
We report here the low-resolution structure of the complex formed by the endo-polygalacturonase from Fusarium phyllophilum and one of the polygalacturonase-inhibiting protein from Phaseolus vulgaris after chemical cross-linking as determined by small-angle x-ray scattering analysis. The inhibitor engages its concave surface of the leucine-rich repeat domain with the enzyme. Both sides of the enzyme active site cleft interact with the inhibitor, accounting for the competitive mechanism of inhibition observed. The structure is in agreement with previous site-directed mutagenesis data and has been further validated with structure-guided mutations and subsequent assay of the inhibitory activity. The structure of the complex may help the design of inhibitors with improved or new recognition capabilities to be used for crop protection.
Figures



References
-
- Bent AF, Mackey D. (2007) Elicitors, effectors, and R genes: the new paradigm and a lifetime supply of questions. Annu Rev Phytopathol 45: 399–436 - PubMed
-
- Boller T, Felix G. (2009) A renaissance of elicitors: perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol 60: 379–406 - PubMed
-
- Bonivento D, Pontiggia D, Di Matteo A, Fernandez-Recio J, Salvi G, Tsernoglou D, Cervone F, Lorenzo GD, Federici L. (2008) Crystal structure of the endopolygalacturonase from the phytopathogenic fungus Colletotrichum lupini and its interaction with polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins. Proteins 70: 294–299 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

