DNA methylation-associated silencing of tumor-suppressor microRNAs in cancer
- PMID: 21860412
- PMCID: PMC3325426
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.354
DNA methylation-associated silencing of tumor-suppressor microRNAs in cancer
Abstract
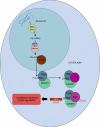
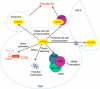
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are recognized as being central players in many biological processes and cellular pathways. Their roles in disease have been highlighted first by observation of their aberrant expression profiles in human tumors, and then by in vitro and in vivo functional studies in transformed cells and model organisms. One of the most commonly observed features of miRNAs in malignancies is a defect in their production. Although several causes may be associated with this phenomenon, such as upstream oncogenic/tumor-suppressor defects and alterations in the miRNA-processing machinery, epigenetic inactivation is the prime suspect. The number of miRNAs with putative growth-inhibitory functions undergoing promoter CpG island hypermethylation in human cancer is growing fast and more detailed biological studies are necessary. The recognition of miR-124a and miR-34b/c as bona fide tumor-suppressor miRNAs undergoing DNA methylation-associated silencing in a wide spectrum of human neoplasms is a good starting point to be followed by other candidate miRNAs. Most importantly, even at this early stage, the transcriptional repression of miRNAs by hypermethylation of their corresponding promoter loci seems to be a common feature of all human tumors. This will have translational consequences for the management of the disease.
Figures

References
-
- Agirre X, Vilas-Zornoza A, Jiménez-Velasco A, Martin-Subero JI, Cordeu L, Gárate L, et al. Epigenetic silencing of the tumor suppressor microRNA Hsa-miR-124a regulates CDK6 expression and confers a poor prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res. 2009;69:4443–4453. - PubMed
-
- Akao Y, Nakagawa Y, Naoe T. Let-7 microRNA functions as a potential growth suppressor in human colon cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2006;29:903–906. - PubMed
-
- Ando T, Yoshida T, Enomoto S, Asada K, Tatematsu M, Ichinose M, et al. DNA methylation of microRNA genes in gastric mucosae of gastric cancer patients: its possible involvement in the formation of epigenetic field defect. Int J Cancer. 2009;124:2367–2374. - PubMed
-
- Azzalin CM, Reichenbach P, Khoriauli L, Giulotto E, Lingner J. Telomeric repeat containing RNA and RNA surveillance factors at mammalian chromosome ends. Science. 2007;318:798–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

