Macrophage-elicited loss of estrogen receptor-α in breast cancer cells via involvement of MAPK and c-Jun at the ESR1 genomic locus
- PMID: 21860415
- PMCID: PMC3223561
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2011.370
Macrophage-elicited loss of estrogen receptor-α in breast cancer cells via involvement of MAPK and c-Jun at the ESR1 genomic locus
Abstract
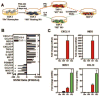
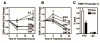
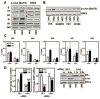
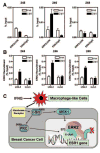
Estrogen receptor-α (ERα, ESR1) is a pivotal transcriptional regulator of breast cancer physiology and is targeted by endocrine therapies. Loss of ERα activity or expression is an indication of endocrine resistance and is associated with increased risk of tumor recurrence and worse prognosis. In this study, we sought to investigate whether elements of the tumor microenvironment, namely macrophages, would impact on ERα and we found that macrophage-derived factors caused loss of ERα expression in breast cancer cells. Conditioned media from macrophages caused activation of several intracellular pathways in breast cancer cells of which c-Src, protein kinase c and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) were essential for loss of ERα expression. Moreover, a prolonged hyperactivation of MAPK was observed. The activation of this kinase cascade resulted in recruitment of extracellular signal regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) directly to chromatin at the ESR1 gene locus in a process that was dependent upon activation and recruitment of the c-Jun transcription factor. Thus, we identify a novel mechanism for loss of ERα expression in breast cancer cells via macrophage activation of kinase cascades in the cancer cells causing transcriptional repression of the ESR1 gene by a direct chromatin action of a c-Jun/ERK2 complex. The findings in this study support an alternative mechanism, not intrinsic to the tumor cell but derived from the cross-talk with the tumor microenvironment, that could lead to endocrine resistance and might be targeted therapeutically to prevent loss of ERα expression in breast tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
F. S., Z. M. E, and B. S. K. have nothing to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in estrogen receptor alpha-positive breast cancer cells in vitro induces an in vivo molecular phenotype of estrogen receptor alpha-negative human breast tumors.Cancer Res. 2006 Apr 1;66(7):3903-11. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-4363. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16585219
-
Hyperactivation of MAPK induces loss of ERalpha expression in breast cancer cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2001 Aug;15(8):1344-59. doi: 10.1210/mend.15.8.0678. Mol Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11463858
-
Genomic collaboration of estrogen receptor alpha and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 in regulating gene and proliferation programs.Mol Cell Biol. 2011 Jan;31(1):226-36. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00821-10. Epub 2010 Oct 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 20956553 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of the estrogen receptor negative phenotype in breast cancer and restoration of antiestrogen response.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Dec 1;13(23):7029-36. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0587. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 18056179
-
AIB1:ERα transcriptional activity is selectively enhanced in aromatase inhibitor-resistant breast cancer cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Jun 15;18(12):3305-15. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-3300. Epub 2012 May 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22550166
Cited by
-
miR-125b controls monocyte adaptation to inflammation through mitochondrial metabolism and dynamics.Blood. 2016 Dec 29;128(26):3125-3136. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-02-697003. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27702798 Free PMC article.
-
Streamlining gene expression analysis: integration of co-culture and mRNA purification.Integr Biol (Camb). 2014 Feb;6(2):224-31. doi: 10.1039/c3ib40136g. Integr Biol (Camb). 2014. PMID: 24413730 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages Promote Subtype Conversion and Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 5;16(3):678. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030678. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339428 Free PMC article.
-
Altered immune signatures in breast cancer lymph nodes with metastases revealed by spatial proteome analyses.J Transl Med. 2025 Apr 10;23(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06415-4. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40211433 Free PMC article.
-
Novel roles for ERK5 and cofilin as critical mediators linking ERα-driven transcription, actin reorganization, and invasiveness in breast cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2014 May;12(5):714-27. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0588. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Mol Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24505128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C, Mantovani A. Immunol Rev. 2008a;222:155–61. - PubMed
-
- Allavena P, Sica A, Solinas G, Porta C, Mantovani A. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008b;66:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Auwerx J. Experientia. 1991;47:22–31. - PubMed
-
- Bayliss J, Hilger A, Vishnu P, Diehl K, El-Ashry D. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:7029–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

