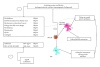
Involvement of activating NK cell receptors and their modulation in pathogen immunity
- PMID: 21860586
- PMCID: PMC3155793
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/152430
Involvement of activating NK cell receptors and their modulation in pathogen immunity
Abstract
Natural Killer (NK) cells are endowed with cell-structure-sensing receptors providing inhibitory protection from self-destruction (inhibitory NK receptors, iNKRs, including killer inhibitory receptors and other molecules) and rapid triggering potential leading to functional cell activation by Toll-like receptors (TLRs), cytokine receptors, and activating NK cell receptors including natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCRs, i.e., NKp46, NKp46, and NKp44). NCR and NKG2D recognize ligands on infected cells which may be endogenous or may directly bind to some structures derived from invading pathogens. In this paper, we address the known direct or indirect interactions between activating receptors and pathogens and their expression during chronic HIV and HCV infections.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of recombinant cytokines on the expression of natural killer cell receptors from patients with TB or/and HIV infection.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e37448. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037448. Epub 2012 Jun 8. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22715368 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Functional Behavior of NKp46-Positive Intrahepatic Natural Killer Cells Against Hepatitis C Virus Reinfection After Liver Transplantation.Transplantation. 2016 Feb;100(2):355-64. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001031. Transplantation. 2016. PMID: 26714120
-
Overexpression of CD158 and NKG2A Inhibitory Receptors and Underexpression of NKG2D and NKp46 Activating Receptors on NK Cells in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Arch Med Res. 2016 Jan;47(1):55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2016.02.001. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Arch Med Res. 2016. PMID: 26876298
-
Regulation of self-ligands for activating natural killer cell receptors.Ann Med. 2013 Jun;45(4):384-94. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2013.792495. Epub 2013 May 23. Ann Med. 2013. PMID: 23701136 Review.
-
Human NK cell response to pathogens.Semin Immunol. 2014 Apr;26(2):152-60. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Semin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24582551 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation and preclinical characterization of an NKp80-Fc fusion protein for redirected cytolysis of natural killer (NK) cells against leukemia.J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 11;290(37):22474-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.678912. Epub 2015 Jul 21. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26198633 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cells: multifaceted players with key roles in hepatitis C immunity.Immunol Rev. 2013 Sep;255(1):68-81. doi: 10.1111/imr.12090. Immunol Rev. 2013. PMID: 23947348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular HCV-core protein induces an immature regulatory phenotype in NK cells: implications for outcome of acute infection.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 30;9(7):e103219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103219. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25076408 Free PMC article.
-
Increased CD56(bright) NK cells in HIV-HCV co-infection and HCV mono-infection are associated with distinctive alterations of their phenotype.Virol J. 2016 Apr 18;13:67. doi: 10.1186/s12985-016-0507-5. Virol J. 2016. PMID: 27091211 Free PMC article.
-
Human herpesviridae methods of natural killer cell evasion.Adv Virol. 2012;2012:359869. doi: 10.1155/2012/359869. Epub 2012 Jul 8. Adv Virol. 2012. PMID: 22829821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moretta L, Biassoni R, Bottino C, Mingari MC, Moretta A. Human NK-cell receptors. Immunology Today. 2000;21(9):420–422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources