Nod2: a key regulator linking microbiota to intestinal mucosal immunity
- PMID: 21861185
- PMCID: PMC3263373
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-011-0802-y
Nod2: a key regulator linking microbiota to intestinal mucosal immunity
Abstract
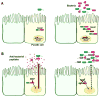
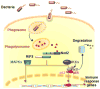
The human intestine harbors a large number of bacteria that are constantly interacting with the intestinal immune system, eliciting non-pathological basal level immune responses. Increasing evidence points to dysbiosis of microbiota in the intestine as an underlying factor in inflammatory bowel disease susceptibility. Loss-of-function mutations in NOD2 are among the stronger genetic factors linked to ileal Crohn's disease. Indeed, Nod2 is a key regulator of microbiota in the intestine, as microflora in the terminal ileum is dysregulated in Nod2-deficient mice. Nod2 is highly expressed in Paneth cells, which are responsible for the regulation of ileal microflora by anti-microbial compounds, and Nod2-deficient ileal intestinal epithelia are unable to kill bacteria efficiently. It is therefore likely that NOD2 mutations in Crohn's disease may increase disease susceptibility by altering interactions between ileal microbiota and mucosal immunity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Xavier RJ, Podolsky DK. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 2007;448:427–434. - PubMed
-
- Sartor RB. Microbial influences in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:577–594. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA, Jr, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Hugot JP, Chamaillard M, Zouali H, Lesage S, Cezard JP, Belaiche J, Almer S, Tysk C, O’Morain CA, Gassull M, et al. Association of NOD2 leucine-rich repeat variants with susceptibility to Crohn’s disease. Nature. 2001;411:599–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

