Epitope mapping of a 95 kDa antigen in complex with antibody by solution-phase amide backbone hydrogen/deuterium exchange monitored by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry
- PMID: 21861454
- PMCID: PMC3173601
- DOI: 10.1021/ac201501z
Epitope mapping of a 95 kDa antigen in complex with antibody by solution-phase amide backbone hydrogen/deuterium exchange monitored by Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry
Abstract
The epitopes of a homohexameric food allergen protein, cashew Ana o 2, identified by two monoclonal antibodies, 2B5 and 1F5, were mapped by solution-phase amide backbone H/D exchange (HDX) coupled with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FTICR MS) and the results were compared to previous mapping by immunological and mutational analyses. Antibody 2B5 defines a conformational epitope, and 1F5 defines a linear epitope. Intact murine IgG antibodies were incubated with recombinant Ana o 2 (rAna o 2) to form antigen-monoclonal antibody (Ag-mAb) complexes. mAb-complexed and uncomplexed (free) rAna o 2 were then subjected to HDX. HDX instrumentation and automation were optimized to achieve high sequence coverage by protease XIII digestion. The regions protected from H/D exchange upon antibody binding overlap and thus confirm the previously identified epitope-bearing segments: the first extension of HDX monitored by mass spectrometry to a full-length antigen-antibody complex in solution.
Figures
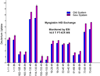



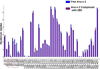
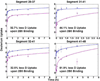
 selected segments of free and complexed rAna o 2. Segments 29–37, 31–41, 32–41 and 41–48 exhibit less deuterium uptake for rAna o 2 complexed with mAb 2B5, thereby defining the 2B5 epitope. Deuterium uptake profiles are similar for segments 160–175 and 282–293. For the binding of mAb 1F5, only one segment (265–289) shows significant protection on complexation, thereby defining its epitope.
selected segments of free and complexed rAna o 2. Segments 29–37, 31–41, 32–41 and 41–48 exhibit less deuterium uptake for rAna o 2 complexed with mAb 2B5, thereby defining the 2B5 epitope. Deuterium uptake profiles are similar for segments 160–175 and 282–293. For the binding of mAb 1F5, only one segment (265–289) shows significant protection on complexation, thereby defining its epitope.
 selected segments of free and complexed rAna o 2. Segments 29–37, 31–41, 32–41 and 41–48 exhibit less deuterium uptake for rAna o 2 complexed with mAb 2B5, thereby defining the 2B5 epitope. Deuterium uptake profiles are similar for segments 160–175 and 282–293. For the binding of mAb 1F5, only one segment (265–289) shows significant protection on complexation, thereby defining its epitope.
selected segments of free and complexed rAna o 2. Segments 29–37, 31–41, 32–41 and 41–48 exhibit less deuterium uptake for rAna o 2 complexed with mAb 2B5, thereby defining the 2B5 epitope. Deuterium uptake profiles are similar for segments 160–175 and 282–293. For the binding of mAb 1F5, only one segment (265–289) shows significant protection on complexation, thereby defining its epitope.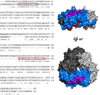
Similar articles
-
Rapid screening for potential epitopes reactive with a polycolonal antibody by solution-phase H/D exchange monitored by FT-ICR mass spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013 Jul;24(7):1016-25. doi: 10.1007/s13361-013-0644-7. Epub 2013 May 17. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013. PMID: 23681851
-
Epitope mapping of 7S cashew antigen in complex with antibody by solution-phase H/D exchange monitored by FT-ICR mass spectrometry.J Mass Spectrom. 2015 Jun;50(6):812-9. doi: 10.1002/jms.3589. J Mass Spectrom. 2015. PMID: 26169135
-
Conformational epitope mapping of Pru du 6, a major allergen from almond nut.Mol Immunol. 2013 Oct;55(3-4):253-63. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.02.004. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23498967
-
Computational Structure Prediction for Antibody-Antigen Complexes From Hydrogen-Deuterium Exchange Mass Spectrometry: Challenges and Outlook.Front Immunol. 2022 May 26;13:859964. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.859964. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35720345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in mass spectrometry-based epitope mapping of protein therapeutics.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022 Jun 5;215:114754. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114754. Epub 2022 Apr 6. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022. PMID: 35427962 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomics for Allergy: from Proteins to the Patients.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016 Sep;16(9):64. doi: 10.1007/s11882-016-0642-5. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016. PMID: 27534655 Review.
-
Characterization of stress-exposed granulocyte colony stimulating factor using ELISA and hydrogen/deuterium exchange mass spectrometry.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014 Oct;25(10):1747-54. doi: 10.1007/s13361-014-0959-z. Epub 2014 Jul 29. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014. PMID: 25070584
-
HDX-MS guided drug discovery: small molecules and biopharmaceuticals.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2014 Oct;28:105-11. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2014.08.007. Epub 2014 Aug 30. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2014. PMID: 25179005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Native Mass Spectrometry, Ion mobility, and Collision-Induced Unfolding Categorize Malaria Antigen/Antibody Binding.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2017 Nov;28(11):2515-2518. doi: 10.1007/s13361-017-1782-0. Epub 2017 Sep 5. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2017. PMID: 28875466 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical reader modules of BAZ1A promote recovery from DNA damage.Nat Commun. 2017 Oct 11;8(1):862. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00866-0. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29021563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Radauer C, Bublin M, Wagner S, Mari A, Breiteneder H. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008;121:847–852. e847. - PubMed
-
- Traidl-Hoffmann C, Jakob T, Behrendt H. J. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. 2009;123:558–566. - PubMed
-
- Chan AC, Carter PJ. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010;10:301–316. - PubMed
-
- Clienti S, Morjaria JB, Basile E, Polosa R. Curr. Allergy Asthma. Rep. 2011;11:253–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

