New target for inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase: 'switch region'
- PMID: 21862392
- PMCID: PMC3196380
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.07.030
New target for inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase: 'switch region'
Abstract
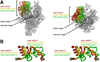
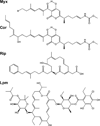
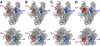
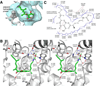
A new drug target - the 'switch region' - has been identified within bacterial RNA polymerase (RNAP), the enzyme that mediates bacterial RNA synthesis. The new target serves as the binding site for compounds that inhibit bacterial RNA synthesis and kill bacteria. Since the new target is present in most bacterial species, compounds that bind to the new target are active against a broad spectrum of bacterial species. Since the new target is different from targets of other antibacterial agents, compounds that bind to the new target are not cross-resistant with other antibacterial agents. Four antibiotics that function through the new target have been identified: myxopyronin, corallopyronin, ripostatin, and lipiarmycin. This review summarizes the switch region, switch-region inhibitors, and implications for antibacterial drug discovery.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Chopra I. Bacterial RNA polymerase: a promising target for the discovery of new antimicrobial agents. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2007;8:600–607. - PubMed
-
- Villain-Guillot P, Bastide L, Gualtieri M, Leonetti J. Progress in targeting bacterial transcription. Drug Discov. Today. 2007;12:200–208. - PubMed
-
- Mariani R, Maffioli S. Bacterial RNA polymerase inhibitors: an organized overview of their structure, derivatives, biological activity and current clinical development status. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009;16:430–454. - PubMed
-
- Floss H, Yu T. Rifamycin: mode of action, resistance, and biosynthesis. Chem. Rev. 2005;105:621–632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

