A marked deficiency in circulating and renal IGF-I peptide does not inhibit compensatory renal enlargement in uninephrectomized mice
- PMID: 21862442
- PMCID: PMC5488277
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ghir.2011.07.008
A marked deficiency in circulating and renal IGF-I peptide does not inhibit compensatory renal enlargement in uninephrectomized mice
Abstract
Objective: Increase in kidney IGF-I levels due to its increased trapping from the circulation was hypothesized to be a key mediator of compensatory renal enlargement. We tested this hypothesis using genetically engineered mice with extremely low circulating IGF-I levels.
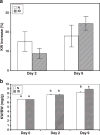
Design: Both IGF-I deficient (ID) and normal (N) mice underwent a uninephrectomy (UNx) and sacrificed 2 or 9days later.
Results: Initial body weight (BW) and kidney weight (KW) were significantly reduced in ID vs. N mice, while KW/BW ratios were similar. KW increased post-UNx to a comparable extent in ID and N mice (125±4 and 118±6% of pre-UNx KW, p<0.05 vs. C). Kidney IGF-I mRNA levels were similar in the ID and N mice and did not change post-UNx. Kidney IGF-I peptide levels pre-UNx were significantly lower in ID vs. N mice (25±5 vs. 305±39ng/g) and increased in both groups after UNx, remaining low in ID mice (45±4 in ID vs 561±64ng/g in N). IGF type 1 receptor phosphorylation was unchanged.
Conclusion: While a severe deficiency of circulating IGF-I impairs body growth, UNx induces a significant and proportional increase in renal mass in ID mice despite markedly decreased kidney IGF-I levels (>90% reduction) and no significant change in receptor phosphorylation. This all suggests that factors other than circulating and locally produced IGF-I are responsible for compensatory renal enlargement.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Serum and renal IGF-I levels after uninephrectomy in the rat.Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1997 Apr;57(2):167-73. doi: 10.1080/00365519709056385. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1997. PMID: 9200276
-
Compensatory kidney growth in estrogen receptor-alpha null mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Feb;290(2):F319-23. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00271.2005. Epub 2005 Sep 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16159896
-
Potential role of IGF-1 in parathyroid hormone-related renal growth induced by high protein diet in uninephrectomized rats.Kidney Int. 1995 Jul;48(1):33-8. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.263. Kidney Int. 1995. PMID: 7564088
-
Early hyperplastic renal growth after uninephrectomy in adult female rats.Endocrinology. 2000 Mar;141(3):932-7. doi: 10.1210/endo.141.3.7353. Endocrinology. 2000. PMID: 10698167
-
Renal dopaminergic mechanisms in renal parenchymal diseases and hypertension.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16 Suppl 1:53-9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/16.suppl_1.53. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001. PMID: 11369822 Review.
Cited by
-
Growth Hormone and IGF1 Actions in Kidney Development and Function.Cells. 2021 Nov 30;10(12):3371. doi: 10.3390/cells10123371. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34943879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood flow-induced angiocrine signals promote organ growth and regeneration.Bioessays. 2025 Feb;47(2):e2400207. doi: 10.1002/bies.202400207. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Bioessays. 2025. PMID: 39529434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human conditions of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) deficiency.J Transl Med. 2012 Nov 14;10:224. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-224. J Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 23148873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I in Management of Neurological Disorders.Neurotox Res. 2022 Jun;40(3):874-883. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00513-7. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Neurotox Res. 2022. PMID: 35476315 Review.
References
-
- Sugaya K, Ogawa Y, Hatano T, Koyama Y, Miyazato T, Naito A, Yonou H, Kagawa H. Compensatory renal hypertrophy and changes of renal function following nephrectomy. Hinyokika Kiyo. 2000;46:235–240. - PubMed
-
- Hostetter TH. Progression of renal disease and renal hypertrophy. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:263–278. - PubMed
-
- Sinuani I, Beberashvili I, Averbukh Z, Cohn M, Gitelman I, Weissgarten J. Mesangial cells initiate compensatory tubular cell hypertrophy. Am J Nephrol. 2010;31:326–331. - PubMed
-
- Mulroney SE, Pesce C. Early hyperplastic renal growth after uninephrectomy in adult female rats. Endocrinology. 2000;141:932–937. - PubMed
-
- Rabkin R, Schaefer F. New concepts: growth hormone, insulin-like growth factor-I and the kidney. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2004;14:270–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

