Isoflurane differentially modulates mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production via forward versus reverse electron transport flow: implications for preconditioning
- PMID: 21862887
- PMCID: PMC3337729
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31822a2316
Isoflurane differentially modulates mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production via forward versus reverse electron transport flow: implications for preconditioning
Abstract
Background: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediate the effects of anesthetic precondition to protect against ischemia and reperfusion injury, but the mechanisms of ROS generation remain unclear. In this study, the authors investigated if mitochondria-targeted antioxidant (mitotempol) abolishes the cardioprotective effects of anesthetic preconditioning. Further, the authors investigated the mechanism by which isoflurane alters ROS generation in isolated mitochondria and submitochondrial particles.
Methods: Rats were pretreated with 0.9% saline, 3.0 mg/kg mitotempol in the absence or presence of 30 min exposure to isoflurane. Myocardial infarction was induced by left anterior descending artery occlusion for 30 min followed by reperfusion for 2 h and infarct size measurements. Mitochondrial ROS production was determined spectrofluorometrically. The effect of isoflurane on enzymatic activity of mitochondrial respiratory complexes was also determined.
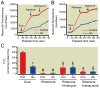
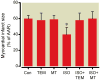
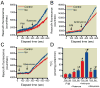
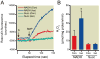
Results: Isoflurane reduced myocardial infarct size (40 ± 9% = mean ± SD) compared with control experiments (60 ± 4%). Mitotempol abolished the cardioprotective effects of anesthetic preconditioning (60 ± 9%). Isoflurane enhanced ROS generation in submitochondrial particles with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (reduced form), but not with succinate, as substrate. In intact mitochondria, isoflurane enhanced ROS production in the presence of rotenone, antimycin A, or ubiquinone when pyruvate and malate were substrates, but isoflurane attenuated ROS production when succinate was substrate. Mitochondrial respiratory experiments and electron transport chain complex assays revealed that isoflurane inhibited only complex I activity.
Conclusions: The results demonstrated that isoflurane produces ROS at complex I and III of the respiratory chain via the attenuation of complex I activity. The action on complex I decreases unfavorable reverse electron flow and ROS release in myocardium during reperfusion.
Figures

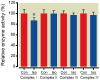
Similar articles
-
Preconditioning by isoflurane is mediated by reactive oxygen species generated from mitochondrial electron transport chain complex III.Anesth Analg. 2004 Nov;99(5):1308-1315. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000134804.09484.5D. Anesth Analg. 2004. PMID: 15502022
-
Isoflurane modulates cardiac mitochondrial bioenergetics by selectively attenuating respiratory complexes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Mar;1837(3):354-65. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Dec 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24355434 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemic defects in the electron transport chain increase the production of reactive oxygen species from isolated rat heart mitochondria.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Feb;294(2):C460-6. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00211.2007. Epub 2007 Dec 12. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18077608
-
Differential effects of complex II on mitochondrial ROS production and their relation to cardioprotective pre- and postconditioning.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 May;1827(5):578-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.01.004. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23333272 Review.
-
Generation of superoxide by the mitochondrial Complex I.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 May-Jun;1757(5-6):553-61. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.03.013. Epub 2006 Apr 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16678117 Review.
Cited by
-
Anesthesia management for percutaneous mitral valve repair in a patient with mitochondrial cardiomyopathy and low cardiac function: a case report.JA Clin Rep. 2024 Aug 8;10(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s40981-024-00734-z. JA Clin Rep. 2024. PMID: 39115707 Free PMC article.
-
Sevoflurane Preconditioning Increases Stress Resistance via IMB-2/DAF-16 in Caenorhabditis Elegans.Dose Response. 2022 Mar 24;20(1):15593258221082886. doi: 10.1177/15593258221082886. eCollection 2022 Jan-Mar. Dose Response. 2022. PMID: 35360453 Free PMC article.
-
QUEST MRI assessment of fetal brain oxidative stress in utero.Neuroimage. 2019 Oct 15;200:601-606. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.05.069. Epub 2019 May 31. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 31158477 Free PMC article.
-
Anaesthetics as cardioprotectants: translatability and mechanism.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Apr;172(8):2051-61. doi: 10.1111/bph.12981. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25322898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis contributes to isoflurane-induced neurotoxicity and learning and memory impairment.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Apr 7;7(1):72. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00454-8. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 33828088 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kersten JR, Schmeling TJ, Pagel PS, Gross GJ, Warltier DC. Isoflurane mimic preconditioning via activation of K(ATP) channels: Reduction of myocardial infarct size with an acute memory phase. Anesthesiology. 1997;87:361–70. - PubMed
-
- Cason BA, Gamperl AK, Slocum RE, Hickey RF. Anesthetic-induced preconditioning: previous administration of isoflurane decreases myocardial infarct size in rabbits. Anesthesiology. 1997;87:1182–90. - PubMed
-
- Ljubkovic M, Mio Y, Marinovic J, Stadnicka A, Warltier DC, Bosnjak ZJ, Bienengraeber M. Isoflurane preconditioning uncouples mitochondria and protects against hypoxia-reoxygenation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292:C1583–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

