Parkinson's disease induced pluripotent stem cells with triplication of the α-synuclein locus
- PMID: 21863007
- PMCID: PMC3265381
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1453
Parkinson's disease induced pluripotent stem cells with triplication of the α-synuclein locus
Abstract
A major barrier to research on Parkinson's disease is inaccessibility of diseased tissue for study. One solution is to derive induced pluripotent stem cells from patients and differentiate them into neurons affected by disease. Triplication of SNCA, encoding α-synuclein, causes a fully penetrant, aggressive form of Parkinson's disease with dementia. α-Synuclein dysfunction is the critical pathogenic event in Parkinson's disease, multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies. Here we produce multiple induced pluripotent stem cell lines from an SNCA triplication patient and an unaffected first-degree relative. When these cells are differentiated into midbrain dopaminergic neurons, those from the patient produce double the amount of α-synuclein protein as neurons from the unaffected relative, precisely recapitulating the cause of Parkinson's disease in these individuals. This model represents a new experimental system to identify compounds that reduce levels of α-synuclein, and to investigate the mechanistic basis of neurodegeneration caused by α-synuclein dysfunction.
© 2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved.
Figures



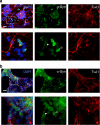

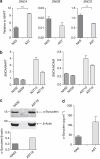
Comment in
-
Parkinson disease: Induced pluripotent stem cells-a new in vitro model to investigate α-synuclein dysfunction in Parkinson disease.Nat Rev Neurol. 2011 Sep 20;7(10):536. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2011.144. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21931347 No abstract available.
-
Pluripotent stem cells with triplication of alpha-synuclein locus.Mov Disord. 2011 Dec;26(14):2480. doi: 10.1002/mds.24056. Mov Disord. 2011. PMID: 22332244 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jankovic J. Parkinson?s disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79, 368–376 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Braak H. & Braak E. Pathoanatomy of Parkinson?s disease. J. Neurol. 247 (Suppl 2), II3–10 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Polymeropoulos M. H. et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson′s disease. Science 276, 2045–2047 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Spillantini M. G. et al. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388, 839–840 (1997). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- G0802462/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K-0911/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- G-0907/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1001253/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- F-0902/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- G-4046/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- 089698/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- F-1002/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/R/00001627/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G108/638/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_G1000735/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/R/00001601/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0802760/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

