Quantification of gene expression after painful nerve injury: validation of optimal reference genes
- PMID: 21863315
- PMCID: PMC3273664
- DOI: 10.1007/s12031-011-9628-x
Quantification of gene expression after painful nerve injury: validation of optimal reference genes
Abstract
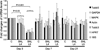
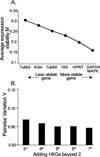
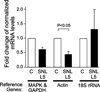
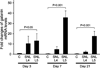
Stably expressed housekeeping genes (HKGs) are necessary for standardization of transcript measurement by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). Peripheral nerve injury disrupts expression of numerous genes in sensory neurons, but the stability of conventional HKGs has not been tested in this context. We examined the stability of candidate HKGs during nerve injury, including the commonly used 18S ribosomal RNA, β-tubulin I and β-tubulin III, actin, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase 1 (HPRT1), and mitogen-activated protein kinase 6 (MAPK6). Total RNA for cDNA synthesis was isolated from dorsal root ganglia of rats at 3, 7, and 21 days following either skin incision alone or spinal nerve ligation, after which the axotomized and adjacent ganglia were analyzed separately. Relative stability of HKGs was determined using statistical algorithms geNorm and NormFinder. Both analyses identified MAPK6 and GAPDH as the two most stable HKGs for normalizing gene expression for qRT-PCR analysis in the context of peripheral nerve injury. Our findings indicate that a prior analysis of HKG expression levels is important for accurate normalization of gene expression in models of nerve injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 2004;64(15):5245–5250. - PubMed
-
- Boeshore KL, Schreiber RC, Vaccariello SA, Sachs HH, Salazar R, Lee J, Ratan RR, Leahy P, Zigmond RE. Novel changes in gene expression following axotomy of a sympathetic ganglion: a microarray analysis. J Neurobiol. 2004;59(2):216–235. - PubMed
-
- Bonefeld BE, Elfving B, Wegener G. Reference genes for normalization: a study of rat brain tissue. Synapse. 2008;62(4):302–309. - PubMed
-
- Cai JH, Deng S, Kumpf SW, Lee PA, Zagouras P, Ryan A, Gallagher DS. Validation of rat reference genes for improved quantitative gene expression analysis using low density arrays. Biotechniques. 2007;42(4):503–512. - PubMed
-
- Costigan M, Befort K, Karchewski L, Griffin RS, D'Urso D, Allchorne A, Sitarski J, Mannion JW, Pratt RE, Woolf CJ. Replicate high-density rat genome oligonucleotide microarrays reveal hundreds of regulated genes in the dorsal root ganglion after peripheral nerve injury. BMC Neurosci. 2002;3:16. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

