Mouse current vocalization threshold measured with a neurospecific nociception assay: the effect of sex, morphine, and isoflurane
- PMID: 21864576
- PMCID: PMC3380423
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.08.011
Mouse current vocalization threshold measured with a neurospecific nociception assay: the effect of sex, morphine, and isoflurane
Abstract
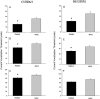
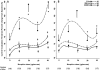
Sine-wave electrical stimulation at frequencies 2000, 250, and 5Hz to respectively evaluate Aβ, Aδ, and C sensory neurons has recently been added to the armamentarium used to evaluate sensory neurons. We developed an automated nociception assay using sine-wave stimulation methodology to determine current vocalization threshold in response to 2000, 250, and 5Hz and examine the effects of sex, analgesics, and anesthetics in mice. At baseline, males had significantly higher mean current vocalization thresholds compared with female mice at 2000, 250, and 5Hz (p≤0.019). By 1h after intrathecal injections of morphine there were significant increases in current vocalization threshold percent changes from baseline that varied with doses (p=0.0001) and frequency used (p<0.0001). Specifically, with increasing doses of morphine, there were significantly greater increases in current vocalization threshold percent changes from baseline in response to 5Hz compared with 250 and 2000Hz stimulation in a significantly ordered pattern: 5Hz>250Hz (p<0.0001) and 250Hz>2000Hz (p=0.0002). Forty-five minutes after exposure, there were no effects of isoflurane on current vocalization thresholds at any frequency. Therefore, our findings suggest that this automated nociception assay using sine-wave stimulation in mice, can be valuable for measurements of the effects of sex, opioids, and anesthetics on the response to electrical stimuli that preferentially stimulate Aβ, Aδ, and C-sensory fibers in vivo. This investigation suggests the validation of this assay and supports its use to examine mechanisms of nociception in mice.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

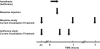

References
-
- Angst MS, Drover DR, Lotsch J, Ramaswamy B, Naidu S, Wada DR, et al. Pharmacodynamics of orally administered sustained-release hydromorphone in humans. Anesthesiology. 2001;94:63–73. - PubMed
-
- Blaszczyk JW, Lapo IB, Werka T, Sadowski B. Differential startle magnitude in mice selected for high and low swim analgesia is not related to difference in nociception. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 2010;70:398–405. - PubMed
-
- Bodnar RJ, Kest B. Sex differences in opioid analgesia, hyperalgesia, tolerance and withdrawal: central mechanisms of action and roles of gonadal hormones. Horm Behav. 2009;58:72–81. - PubMed
-
- Chesler EJ, Wilson SG, Lariviere WR, Rodriguez-Zas SL, Mogil JS. Identification and ranking of genetic and laboratory environment factors influencing a behavioral trait, thermal nociception, via computational analysis of a large data archive. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2002;26:907–23. - PubMed
-
- Fairbanks CA. Spinal delivery of analgesics in experimental models of pain and analgesia. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55:1007–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

