CT, MRI and PET imaging in peritoneal malignancy
- PMID: 21865109
- PMCID: PMC3205758
- DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2011.0016
CT, MRI and PET imaging in peritoneal malignancy
Abstract
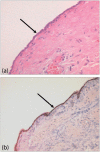
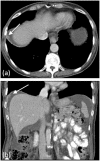
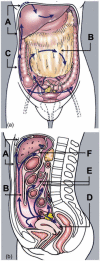
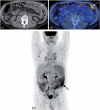
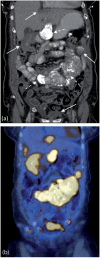
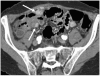
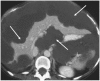
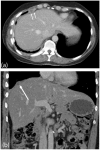
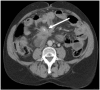
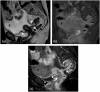
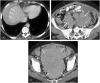
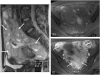
Imaging plays a vital role in the evaluation of patients with suspected or proven peritoneal malignancy. Nevertheless, despite significant advances in imaging technology and protocols, assessment of peritoneal pathology remains challenging. The combination of complex peritoneal anatomy, an extensive surface area that may host tumour deposits and the considerable overlap of imaging appearances of various peritoneal diseases often makes interpretation difficult. Contrast-enhanced multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) remains the most versatile tool in the imaging of peritoneal malignancy. However, conventional and emerging magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET)/CT techniques offer significant advantages over MDCT in detection and surveillance. This article reviews established and new techniques in CT, MRI and PET imaging in both primary and secondary peritoneal malignancies and provides an overview of peritoneal anatomy, function and modes of disease dissemination with illustration of common sites and imaging features of peritoneal malignancy.
Figures




References
-
- Meyers MA. Distribution of intra-abdominal malignant seeding: dependency on dynamics of flow of ascitic fluid. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1973;119:198–206. - PubMed
-
- Standring S. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 39th ed. Churchill Livingstone; 2004. Peritoneum and peritoneal cavity.
-
- DeMeo JH, Fulcher AS, Austin RF., Jr Anatomic CT demonstration of the peritoneal spaces, ligaments, and mesenteries: normal and pathologic processes. Radiographics. 1995;15:755–70. - PubMed
-
- Gore RM, Levine LS. Textbook of gastrointestinal radiology. 3rd ed. Saunders; 2007. Peritoneal and retroperitoneal anatomy; pp. 2071–97.
