Mitochondrial Ccs1 contains a structural disulfide bond crucial for the import of this unconventional substrate by the disulfide relay system
- PMID: 21865601
- PMCID: PMC3192856
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0296
Mitochondrial Ccs1 contains a structural disulfide bond crucial for the import of this unconventional substrate by the disulfide relay system
Abstract
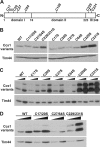
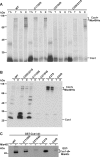
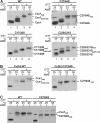
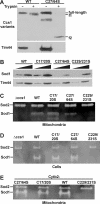
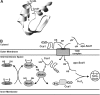
The copper chaperone for superoxide dismutase 1 (Ccs1) provides an important cellular function against oxidative stress. Ccs1 is present in the cytosol and in the intermembrane space (IMS) of mitochondria. Its import into the IMS depends on the Mia40/Erv1 disulfide relay system, although Ccs1 is, in contrast to typical substrates, a multidomain protein and lacks twin Cx(n)C motifs. We report on the molecular mechanism of the mitochondrial import of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ccs1 as the first member of a novel class of unconventional substrates of the disulfide relay system. We show that the mitochondrial form of Ccs1 contains a stable disulfide bond between cysteine residues C27 and C64. In the absence of these cysteines, the levels of Ccs1 and Sod1 in mitochondria are strongly reduced. Furthermore, C64 of Ccs1 is required for formation of a Ccs1 disulfide intermediate with Mia40. We conclude that the Mia40/Erv1 disulfide relay system introduces a structural disulfide bond in Ccs1 between the cysteine residues C27 and C64, thereby promoting mitochondrial import of this unconventional substrate. Thus the disulfide relay system is able to form, in addition to double disulfide bonds in twin Cx(n)C motifs, single structural disulfide bonds in complex protein domains.
Figures

References
-
- Allen S, Balabanidou V, Sideris DP, Lisowsky T, Tokatlidis K. Erv1 mediates the Mia40-dependent protein import pathway and provides a functional link to the respiratory chain by shuttling electrons to cytochrome c. J Mol Biol. 2005;353:937–944. - PubMed
-
- Arnesano F, Balatri E, Banci L, Bertini I, Winge DR. Folding studies of Cox17 reveal an important interplay of cysteine oxidation and copper binding. Structure. 2005;13:713–722. - PubMed
-
- Banci L, Bertini I, Cefaro C, Ciofi-Baffoni S, Gallo A, Martinelli M, Sideris DP, Katrakili N, Tokatlidis K. MIA40 is an oxidoreductase that catalyzes oxidative protein folding in mitochondria. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009;16:198–206. - PubMed
-
- Bien M, Longen S, Wagener N, Chwalla I, Herrmann JM, Riemer J. Mitochondrial disulfide bond formation is driven by intersubunit electron transfer in Erv1 and proofread by glutathione. Mol Cell. 2010;37:516–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

