Vertical decomposition with Genetic Algorithm for Multiple Sequence Alignment
- PMID: 21867510
- PMCID: PMC3180391
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-353
Vertical decomposition with Genetic Algorithm for Multiple Sequence Alignment
Abstract
Background: Many Bioinformatics studies begin with a multiple sequence alignment as the foundation for their research. This is because multiple sequence alignment can be a useful technique for studying molecular evolution and analyzing sequence structure relationships.
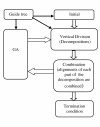
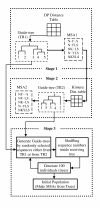
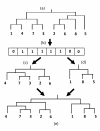
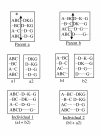
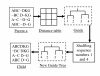
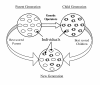
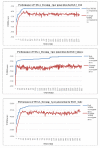
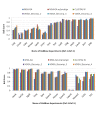
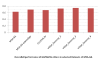
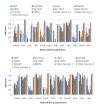
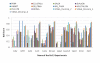
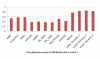
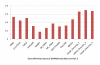
Results: In this paper, we have proposed a Vertical Decomposition with Genetic Algorithm (VDGA) for Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA). In VDGA, we divide the sequences vertically into two or more subsequences, and then solve them individually using a guide tree approach. Finally, we combine all the subsequences to generate a new multiple sequence alignment. This technique is applied on the solutions of the initial generation and of each child generation within VDGA. We have used two mechanisms to generate an initial population in this research: the first mechanism is to generate guide trees with randomly selected sequences and the second is shuffling the sequences inside such trees. Two different genetic operators have been implemented with VDGA. To test the performance of our algorithm, we have compared it with existing well-known methods, namely PRRP, CLUSTALX, DIALIGN, HMMT, SB_PIMA, ML_PIMA, MULTALIGN, and PILEUP8, and also other methods, based on Genetic Algorithms (GA), such as SAGA, MSA-GA and RBT-GA, by solving a number of benchmark datasets from BAliBase 2.0.
Conclusions: The experimental results showed that the VDGA with three vertical divisions was the most successful variant for most of the test cases in comparison to other divisions considered with VDGA. The experimental results also confirmed that VDGA outperformed the other methods considered in this research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An enhanced algorithm for multiple sequence alignment of protein sequences using genetic algorithm.EXCLI J. 2015 Dec 15;14:1232-55. doi: 10.17179/excli2015-302. eCollection 2015. EXCLI J. 2015. PMID: 27065770 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing multiple sequence alignments using a genetic algorithm based on three objectives: structural information, non-gaps percentage and totally conserved columns.Bioinformatics. 2013 Sep 1;29(17):2112-21. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt360. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23793754
-
A Novel Approach to Multiple Sequence Alignment Using Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithm Based on Decomposition.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2016 Mar;20(2):717-27. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2015.2403397. Epub 2015 Feb 12. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2016. PMID: 25700475
-
A review on multiple sequence alignment from the perspective of genetic algorithm.Genomics. 2017 Oct;109(5-6):419-431. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2017.06.007. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28669847 Review.
-
Homology assessment and molecular sequence alignment.J Biomed Inform. 2006 Feb;39(1):18-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2005.11.005. Epub 2005 Dec 9. J Biomed Inform. 2006. PMID: 16380300 Review.
Cited by
-
Review on the Application of Machine Learning Algorithms in the Sequence Data Mining of DNA.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Sep 4;8:1032. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.01032. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33015010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Naturally selecting solutions: the use of genetic algorithms in bioinformatics.Bioengineered. 2013 Sep-Oct;4(5):266-78. doi: 10.4161/bioe.23041. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Bioengineered. 2013. PMID: 23222169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IBBOMSA: An Improved Biogeography-based Approach for Multiple Sequence Alignment.Evol Bioinform Online. 2016 Oct 27;12:237-246. doi: 10.4137/EBO.S40457. eCollection 2016. Evol Bioinform Online. 2016. PMID: 27812276 Free PMC article.
-
Disease Sequences High-Accuracy Alignment Based on the Precision Medicine.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Feb 22;2018:1718046. doi: 10.1155/2018/1718046. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29682519 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Foraging Optimization -Genetic Algorithm for Multiple Sequence Alignment with Multi-Objectives.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 18;7(1):8833. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09499-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28821841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stoye J, Perrey SW, Dress AWM. Improving the divide-and-conquer approach to sum-of-pairs multiple sequence alignment. App Maths Letters. 1997;10:67–73.
-
- Bonizzoni P, Vedova GD. The complexity of multiple sequence alignment with SP-score that is a metric. Theor Comp Sci. 2001;259:63–79. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3975(99)00324-2. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

