Association between RUNX3 promoter methylation and gastric cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 21867527
- PMCID: PMC3183003
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-230X-11-92
Association between RUNX3 promoter methylation and gastric cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Runt-related transcription factor 3 (RUNX3) is a member of the runt-domain family of transcription factors and has been reported to be a candidate tumor suppressor in gastric cancer. However, the association between RUNX3 promoter methylation and gastric cancer remains unclear.
Methods: We systematically reviewed studies of RUNX3 promoter methylation and gastric cancer published in English or Chinese from January 2000 to January 2011, and quantified the association between RUNX3 promoter methylation and gastric cancer using meta-analysis methods.
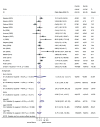
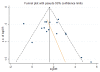
Results: A total of 1740 samples in 974 participants from seventeen studies were included in the meta-analysis. A significant association was observed between RUNX3 promoter methylation and gastric cancer, with an aggregated odds ratio (OR) of 5.63 (95%CI 3.15, 10.07). There was obvious heterogeneity among studies. Subgroup analyses (including by tissue origin, country and age), meta-regression were performed to determine the source of the heterogeneity. Meta-regression showed that the trend in ORs was inversely correlated with age. No publication bias was detected. The ORs for RUNX3 methylation in well-differentiated vs undifferentiated gastric cancers, and in intestinal-type vs diffuse-type carcinomas were 0.59 (95%CI: 0.30, 1.16) and 2.62 (95%CI: 1.33, 5.14), respectively. There were no significant differences in RUNX3 methylation in cancer tissues in relation to age, gender, TNM stage, invasion of tumors into blood vessel or lymphatic ducts, or tumor stage.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis identified a strong association between methylation of the RUNX3 promoter and gastric cancer, confirming the role of RUNX3 as a tumor suppressor gene.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association between runt-related transcription factor 3 gene promoter methylation and gastric cancer: A meta-analysis.J Cancer Res Ther. 2016 Oct;12(Supplement):50-53. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.191630. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27721253
-
Site-specific Hypermethylation of RUNX3 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Gastric Cancer.Arch Med Res. 2016 May;47(4):285-92. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2016.07.011. Arch Med Res. 2016. PMID: 27664488
-
Association of promoter methylation of RUNX3 gene with the development of esophageal cancer: a meta analysis.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 17;9(9):e107598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107598. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25229459 Free PMC article.
-
Stepwise cumulation of RUNX3 methylation mediated by Helicobacter pylori infection contributes to gastric carcinoma progression.Cancer. 2012 Nov 15;118(22):5507-17. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27604. Epub 2012 May 10. Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22576578
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of runt-related transcription factor 3 gene promoter hypermethylation and risk of gastric cancer.J Cancer Res Ther. 2014 Dec;10 Suppl:310-3. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.151539. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25693942
Cited by
-
RUNX3 promoter hypermethylation is frequent in leukaemia cell lines and associated with acute myeloid leukaemia inv(16) subtype.Br J Haematol. 2015 May;169(3):344-51. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13299. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Br J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25612675 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Bacteria and their Metabolites: Which One Is the Defendant for Colorectal Cancer?Microorganisms. 2019 Nov 13;7(11):561. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7110561. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31766208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbiota impact on the epigenetic regulation of colorectal cancer.Trends Mol Med. 2013 Dec;19(12):714-25. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Trends Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 24051204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An inverse relationship between the expression of the gastric tumor suppressor RUNX3 and infection with Helicobacter pylori in gastric epithelial dysplasia.Gut Liver. 2013 Nov;7(6):688-95. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2013.7.6.688. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Gut Liver. 2013. PMID: 24312710 Free PMC article.
-
Lineage-specific RUNX3 hypomethylation marks the preneoplastic immune component of gastric cancer.Oncogene. 2015 May 28;34(22):2856-66. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.233. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25088199 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li QL, Ito K, Sakakura C, Fukamachi H, Inoue K, Chi XZ, Lee KY, Nomura S, Lee CW, Han SB, Kim HM, Kim WJ, Yamamoto H, Yamashita N, Yano T, Ikeda T, Itohara S, Inazawa J, Abe T, Hagiwara A, Yamagishi H, Ooe A, Kaneda A, Sugimura T, Ushijima T, Bae SC, Ito Y. Causal relationship between the loss of RUNX3 expression and gastric cancer. Cell. 2002;109(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00690-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

