Global transcriptome analysis of two ameiotic1 alleles in maize anthers: defining steps in meiotic entry and progression through prophase I
- PMID: 21867558
- PMCID: PMC3180651
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-120
Global transcriptome analysis of two ameiotic1 alleles in maize anthers: defining steps in meiotic entry and progression through prophase I
Abstract
Background: Developmental cues to start meiosis occur late in plants. Ameiotic1 (Am1) encodes a plant-specific nuclear protein (AM1) required for meiotic entry and progression through early prophase I. Pollen mother cells (PMCs) remain mitotic in most am1 mutants including am1-489, while am1-praI permits meiotic entry but PMCs arrest at the leptotene/zygotene (L/Z) transition, defining the roles of AM1 protein in two distinct steps of meiosis. To gain more insights into the roles of AM1 in the transcriptional pre-meiotic and meiotic programs, we report here an in depth analysis of gene expression alterations in carefully staged anthers at 1 mm (meiotic entry) and 1.5 mm (L/Z) caused by each of these am1 alleles.
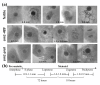
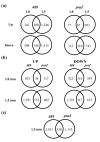
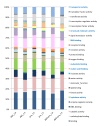
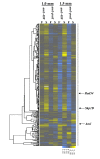
Results: 1.0 mm and 1.5 mm anthers of am1-489 and am1-praI were profiled in comparison to fertile siblings on Agilent® 4 × 44 K microarrays. Both am1-489 and am1-praI anthers are cytologically normal at 1.0 mm and show moderate transcriptome alterations. At the 1.5-mm stage both mutants are aberrant cytologically, and show more drastic transcriptome changes. There are substantially more absolute On/Off and twice as many differentially expressed genes (sterile versus fertile) in am1-489 than in am1-praI. At 1.5 mm a total of 4,418 genes are up- or down-regulated in either am1-489 or am1-praI anthers. These are predominantly stage-specific transcripts. Many putative meiosis-related genes were found among them including a small subset of allele-specific, mis-regulated genes specific to the PMCs. Nearly 60% of transcriptome changes in the set of transcripts mis-regulated in both mutants (N = 530) are enriched in PMCs, and only 1% are enriched in the tapetal cell transcriptome. All array data reported herein will be deposited and accessible at MaizeGDB http://www.maizegdb.org/.
Conclusions: Our analysis of anther transcriptome modulations by two distinct am1 alleles, am1-489 and am1-praI, redefines the role of AM1 as a modulator of expression of a subset of meiotic genes, important for meiotic progression and provided stage-specific insights into the genetic networks associated with meiotic entry and early prophase I progression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Maize AMEIOTIC1 is essential for multiple early meiotic processes and likely required for the initiation of meiosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 3;106(9):3603-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810115106. Epub 2009 Feb 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19204280 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the ameiotic1 gene in the initiation of meiosis and in subsequent meiotic events in maize.Genetics. 1993 Dec;135(4):1151-66. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.4.1151. Genetics. 1993. PMID: 8307330 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the role of the maize ameiotic1 locus.Genetics. 1997 Nov;147(3):1339-50. doi: 10.1093/genetics/147.3.1339. Genetics. 1997. PMID: 9383075 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-meiotic anther development.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2019;131:239-256. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30612619 Review.
-
The meiotic transcriptome architecture of plants.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Jun 5;5:220. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00220. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24926296 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The transcriptome landscape of early maize meiosis.BMC Plant Biol. 2014 May 3;14:118. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-14-118. BMC Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 24885405 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic landscape of prophase I sunflower male meiocytes.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Jun 16;5:277. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00277. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24982667 Free PMC article.
-
Cytological characterization and allelism testing of anther developmental mutants identified in a screen of maize male sterile lines.G3 (Bethesda). 2013 Feb;3(2):231-49. doi: 10.1534/g3.112.004465. Epub 2013 Feb 1. G3 (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 23390600 Free PMC article.
-
Rye (Secale cereale) supernumerary (B) chromosomes associated with heat tolerance during early stages of male sporogenesis.Ann Bot. 2017 Feb;119(3):325-337. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcw206. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Ann Bot. 2017. PMID: 27818381 Free PMC article.
-
Maize germinal cell initials accommodate hypoxia and precociously express meiotic genes.Plant J. 2014 Feb;77(4):639-52. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12414. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Plant J. 2014. PMID: 24387628 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

