High field magnetic resonance microscopy of the human hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease: quantitative imaging and correlation with iron
- PMID: 21867761
- PMCID: PMC3690369
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.08.019
High field magnetic resonance microscopy of the human hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease: quantitative imaging and correlation with iron
Abstract
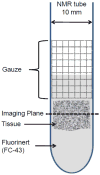
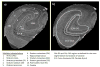
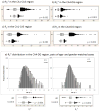
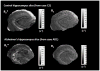
We report R(2) and R(2) in human hippocampus from five unfixed post-mortem Alzheimer's disease (AD) and three age-matched control cases. Formalin-fixed tissues from opposing hemispheres in a matched AD and control were included for comparison. Imaging was performed in a 600MHz (14T) vertical bore magnet at MR microscopy resolution to obtain R(2) and R(2) (62 μm×62 μm in-plane, 80 μm slice thickness), and R(1) at 250 μm isotropic resolution. R(1), R(2) and R(2) maps were computed for individual slices in each case, and used to compare subfields between AD and controls. The magnitudes of R(2) and R(2) changed very little between AD and control, but their variances in the Cornu Ammonis and dentate gyrus were significantly higher in AD compared for controls (p<0.001). To investigate the relationship between tissue iron and MRI parameters, each tissue block was cryosectioned at 30 μm in the imaging plane, and iron distribution was mapped using synchrotron microfocus X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy. A positive correlation of R(2) and R(2)* with iron was demonstrated. While studies with fixed tissues are more straightforward to conduct, fixation can alter iron status in tissues, making measurement of unfixed tissue relevant. To our knowledge, these data represent an advance in quantitative imaging of hippocampal subfields in unfixed tissue, and the methods facilitate direct analysis of the relationship between MRI parameters and iron. The significantly increased variance in AD compared for controls warrants investigation at lower fields and in-vivo, to determine if this parameter is clinically relevant.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


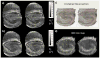
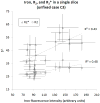
References
-
- Bartzokis G, Cummings JL, Sultzer D, Henderson VW, Nuechterlein KH, Mintz J. White matter structural integrity in healthy aging adults and patients with Alzheimer disease: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Neurol. 2003;60:393–398. - PubMed
-
- Bartzokis G, Lu PH, Mintz J. Quantifying age-related myelin breakdown with MRI: novel therapeutic targets for preventing cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2004;6:S53–59. - PubMed
-
- Bartzokis G, Sultzer D, Cummings J, Holt LE, Hance DB, Henderson VW, Mintz J. In vivo evaluation of brain iron in Alzheimer disease using magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57:47–53. - PubMed
-
- Brar S, Henderson D, Schenck J, Zimmerman EA. Iron accumulation in the substantia nigra of patients with Alzheimer disease and parkinsonism. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:371–374. - PubMed
-
- Brass SD, Chen NK, Mulkern RV, Bakshi R. Magnetic resonance imaging of iron deposition in neurological disorders. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;17:31–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

