Vitamin A supplements for preventing mortality, illness, and blindness in children aged under 5: systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 21868478
- PMCID: PMC3162042
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.d5094
Vitamin A supplements for preventing mortality, illness, and blindness in children aged under 5: systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To determine if vitamin A supplementation is associated with reductions in mortality and morbidity in children aged 6 months to 5 years.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Two reviewers independently assessed studies for inclusion. Data were double extracted; discrepancies were resolved by discussion. Meta-analyses were performed for mortality, illness, vision, and side effects.
Data sources: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in the Cochrane Library, Medline, Embase, Global Health, Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences, metaRegister of Controlled Trials, and African Index Medicus. Databases were searched to April 2010 without restriction by language or publication status.
Eligibility criteria for selecting studies: Randomised trials of synthetic oral vitamin A supplements in children aged 6 months to 5 years. Studies of children with current illness (such as diarrhoea, measles, and HIV), studies of children in hospital, and studies of food fortification or β carotene were excluded.
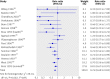
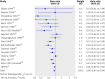
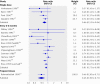
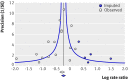
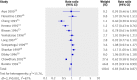
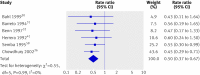
Results: 43 trials with about 215,633 children were included. Seventeen trials including 194,483 participants reported a 24% reduction in all cause mortality (rate ratio=0.76, 95% confidence interval 0.69 to 0.83). Seven trials reported a 28% reduction in mortality associated with diarrhoea (0.72, 0.57 to 0.91). Vitamin A supplementation was associated with a reduced incidence of diarrhoea (0.85, 0.82 to 0.87) and measles (0.50, 0.37 to 0.67) and a reduced prevalence of vision problems, including night blindness (0.32, 0.21 to 0.50) and xerophthalmia (0.31, 0.22 to 0.45). Three trials reported an increased risk of vomiting within the first 48 hours of supplementation (2.75, 1.81 to 4.19).
Conclusions: Vitamin A supplementation is associated with large reductions in mortality, morbidity, and vision problems in a range of settings, and these results cannot be explained by bias. Further placebo controlled trials of vitamin A supplementation in children between 6 and 59 months of age are not required. However, there is a need for further studies comparing different doses and delivery mechanisms (for example, fortification). Until other sources are available, vitamin A supplements should be given to all children at risk of deficiency, particularly in low and middle income countries.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures


Comment in
-
Improving child survival through vitamin A supplementation.BMJ. 2011 Aug 25;343:d5294. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5294. BMJ. 2011. PMID: 21868480 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bates CJ. Vitamin A. Lancet 1995;345:31-5. - PubMed
-
- Sommer A, West KP. Vitamin A deficiency: health, survival, and vision. Oxford University Press, 1996.
-
- Rice AL, West KP Jr, Black RE. Vitamin A deficiency. Global and regional burden of disease attributable to selected major risk factors. Vol 1. World Health Organization, 2004.
-
- Black RE, Cousens S, Johnson HL, Lawn JE, Rudan I, Bassani DG, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of child mortality in 2008: a systematic analysis. Lancet 2010;375:1969-87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
