p53 activation of mesenchymal stromal cells partially abrogates microenvironment-mediated resistance to FLT3 inhibition in AML through HIF-1α-mediated down-regulation of CXCL12
- PMID: 21868571
- PMCID: PMC3204912
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-334136
p53 activation of mesenchymal stromal cells partially abrogates microenvironment-mediated resistance to FLT3 inhibition in AML through HIF-1α-mediated down-regulation of CXCL12
Abstract
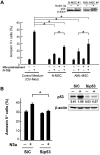
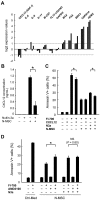
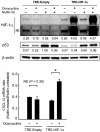
Fms-like tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3) inhibitors have been used to overcome the dismal prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) with FLT3 mutations. Clinical results with FLT3 inhibitor monotherapy have shown that bone marrow responses are commonly less pronounced than peripheral blood responses. We investigated the role of p53 in bone marrow stromal cells in stromal cell-mediated resistance to FLT3 inhibition in FLT3 mutant AML. While the FLT3 inhibitor FI-700 induced apoptosis in FLT3 mutant AML cells, apoptosis induction was diminished under stromal coculture conditions. Protection appeared to be mediated, in part, by CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 signaling. The protective effect of stromal cells was significantly reduced by pre-exposure to the HDM2 inhibitor Nutlin-3a. p53 activation by Nutlin-3a was not cytotoxic to stromal cells, but reduced CXCL12 mRNA levels and secretion of CXCL12 partially through p53-mediated HIF-1α down-regulation. Results show that p53 activation in stroma cells blunts stroma cell-mediated resistance to FLT3 inhibition, in part through down-regulation of CXCL12. This is the first report of Nutlin effect on the bone marrow environment. We suggest that combinations of HDM2 antagonists and FLT3 inhibitors may be effective in clinical trials targeting mutant FLT3 leukemias.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Targeting the leukemia microenvironment by CXCR4 inhibition overcomes resistance to kinase inhibitors and chemotherapy in AML.Blood. 2009 Jun 11;113(24):6215-24. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-158311. Epub 2008 Oct 27. Blood. 2009. PMID: 18955566 Free PMC article.
-
Selective FLT3 inhibitor FI-700 neutralizes Mcl-1 and enhances p53-mediated apoptosis in AML cells with activating mutations of FLT3 through Mcl-1/Noxa axis.Leukemia. 2010 Jan;24(1):33-43. doi: 10.1038/leu.2009.212. Epub 2009 Oct 15. Leukemia. 2010. PMID: 19946262
-
Bone marrow stroma-mediated resistance to FLT3 inhibitors in FLT3-ITD AML is mediated by persistent activation of extracellular regulated kinase.Br J Haematol. 2014 Jan;164(1):61-72. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12599. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Br J Haematol. 2014. PMID: 24116827 Free PMC article.
-
The Future of Targeting FLT3 Activation in AML.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2017 Jun;12(3):153-167. doi: 10.1007/s11899-017-0381-2. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2017. PMID: 28421420 Review.
-
Targeting FLT3 for the treatment of leukemia.Semin Hematol. 2008 Jul;45(3 Suppl 2):S17-21. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2008.07.007. Semin Hematol. 2008. PMID: 18760705 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human extramedullary bone marrow in mice: a novel in vivo model of genetically controlled hematopoietic microenvironment.Blood. 2012 May 24;119(21):4971-80. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-11-389957. Epub 2012 Apr 5. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22490334 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric analysis of etoposide exposed mesenchymal stem cells and Fanconi anemia cells: implications in development of secondary myeloid malignancy.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Dec;23(8):4511-4524. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01087-0. Epub 2023 May 13. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37179284
-
Combined inhibition of MDM2 and BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase targets chronic myeloid leukemia stem/progenitor cells in a murine model.Haematologica. 2020 May;105(5):1274-1284. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.219261. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Haematologica. 2020. PMID: 31371419 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting p53-p21 signaling to enhance mesenchymal stem cell regenerative potential.Regen Ther. 2025 Apr 7;29:352-363. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2025.03.007. eCollection 2025 Jun. Regen Ther. 2025. PMID: 40248767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concomitant inhibition of DNA methyltransferase and BCL-2 protein function synergistically induce mitochondrial apoptosis in acute myelogenous leukemia cells.Ann Hematol. 2012 Dec;91(12):1861-70. doi: 10.1007/s00277-012-1537-8. Epub 2012 Aug 15. Ann Hematol. 2012. PMID: 22893484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stirewalt DL, Radich JP. The role of FLT3 in haematopoietic malignancies. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3(9):650–665. - PubMed
-
- Yanada M, Matsuo K, Suzuki T, Kiyoi H, Naoe T. Prognostic significance of FLT3 internal tandem duplication and tyrosine kinase domain mutations for acute myeloid leukemia: a meta-analysis. Leukemia. 2005;19(8):1345–1349. - PubMed
-
- Whitman SP, Ruppert AS, Radmacher MD, et al. FLT3 D835/I836 mutations are associated with poor disease-free survival and a distinct gene-expression signature among younger adults with de novo cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia lacking FLT3 internal tandem duplications. Blood. 2008;111(3):1552–1559. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choudhary C, Brandts C, Schwable J, et al. Activation mechanisms of STAT5 by oncogenic Flt3-ITD. Blood. 2007;110(1):370–374. - PubMed
-
- Scheijen B, Ngo HT, Kang H, Griffin JD. FLT3 receptors with internal tandem duplications promote cell viability and proliferation by signaling through Foxo proteins. Oncogene. 2004;23(19):3338–3349. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

