Gain and loss of function for glutathione synthesis: impact on advanced atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
- PMID: 21868708
- PMCID: PMC3415243
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.229765
Gain and loss of function for glutathione synthesis: impact on advanced atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice
Abstract
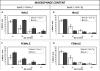
Objective: Glutamate-cysteine ligase (GCL) is the rate-limiting step in glutathione synthesis. The enzyme is a heterodimer composed of a catalytic subunit, GCLC, and a modifier subunit, GCLM. We generated apolipoprotein E (apoE)-/- mice deficient in GCLM (apoE-/-/Gclm-/-) and transgenic mice that overexpress GCLC specifically in macrophages (apoE-/-/Gclc-Tg) to test the hypothesis that significantly altering the availability of glutathione has a measurable impact on both the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis.
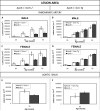
Methods and results: Atherosclerotic plaque size and composition were measured in the innominate artery in chow-fed male and female mice at 20, 30, 40, and 50 weeks of age and in the aortic sinus at 40 and 50 weeks of age. The apoE-/-/Gclm-/- mice more rapidly developed complex lesions, whereas the apoE-/-/Gclc-Tg mice had reduced lesion development compared with the littermate apoE-/- control mice. Transplantation of bone marrow from the apoE-/-/Gclm-/- and apoE-/-/Gclc-Tg mice into apoE-/- mice with established lesions also stimulated or inhibited further lesion development at 30 weeks posttransplant.
Conclusion: Gain and loss of function in the capacity to synthesize glutathione especially in macrophages has reciprocal effects on the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis at multiple sites in apoE-/- mice.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fibronectin Containing Extra Domain A Induces Plaque Destabilization in the Innominate Artery of Aged Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Mar;38(3):500-508. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.310345. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29326316 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic CGI-58 expression in macrophages alleviates the atherosclerotic lesion development in ApoE knockout mice.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Dec;1841(12):1683-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.08.014. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 25178844
-
CCN4 (WISP-1) reduces apoptosis and atherosclerotic plaque burden in an ApoE mouse model.Atherosclerosis. 2024 Oct;397:118570. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2024.118570. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Atherosclerosis. 2024. PMID: 39276419 Free PMC article.
-
FFAR4 Deficiency Increases Necrotic Cores in Advanced Lesions of ApoE-/- Mice-Brief Report.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025 May;45(5):675-682. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.322371. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025. PMID: 40047073
-
The fat-fed apolipoprotein E knockout mouse brachiocephalic artery in the study of atherosclerotic plaque rupture.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:379069. doi: 10.1155/2011/379069. Epub 2010 Nov 7. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21076539 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Re-Visiting Antioxidant Therapy in Murine Advanced Atherosclerosis with Brussels Chicory, a Typical Vegetable in Mediterranean Diets.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 6;15(4):832. doi: 10.3390/nu15040832. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36839190 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms in Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase, a Key Enzyme of Glutathione Biosynthesis, on Ischemic Stroke Risk and Brain Infarct Size.Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 18;12(4):602. doi: 10.3390/life12040602. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455093 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulated cellular metabolism in atherosclerosis: mediators and therapeutic opportunities.Nat Metab. 2024 Apr;6(4):617-638. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01015-w. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Nat Metab. 2024. PMID: 38532071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heme oxygenase-1, oxidation, inflammation, and atherosclerosis.Front Pharmacol. 2012 Jul 19;3:119. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00119. eCollection 2012. Front Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22833723 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants in the Fight Against Atherosclerosis: Is This a Dead End?Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2018 May 21;20(7):36. doi: 10.1007/s11883-018-0737-7. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2018. PMID: 29781062 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dalton TP, Chen Y, Schneider SN, Nebert DW, Shertzer HG. Genetically altered mice to evaluate glutathione homeostasis in health and disease. Free Radic Biol Medq. 2004;37:1511–1526. - PubMed
-
- Meister A, Anderson ME. Glutathione. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:711–760. - PubMed
-
- Sierra-Rivera E, Dasouki M, Summar ML, Krishnamani MR, Meredith M, Rao PN, Phillips JA, 3rd, Freeman ML. Assignment of the human gene (glclr) that encodes the regulatory subunit of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase to chromosome 1p21. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1996;72:252–254. - PubMed
-
- Sierra-Rivera E, Summar ML, Dasouki M, Krishnamani MR, Phillips JA, Freeman ML. Assignment of the gene (glclc) that encodes the heavy subunit of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase to human chromosome 6. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1995;70:278–279. - PubMed
-
- Tsuchiya K, Mulcahy RT, Reid LL, Disteche CM, Kavanagh TJ. Mapping of the glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit gene (glclc) to human chromosome 6p12 and mouse chromosome 9d-e and of the regulatory subunit gene (glclr) to human chromosome 1p21–p22 and mouse chromosome 3h1-3. Genomics. 1995;30:630–632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

