Polyamines in aging and disease
- PMID: 21869457
- PMCID: PMC3184975
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.100361
Polyamines in aging and disease
Abstract
Polyamines are polycations that interact with negatively charged molecules such as DNA, RNA and proteins. They play multiple roles in cell growth, survival and proliferation. Changes in polyamine levels have been associated with aging and diseases. Their levels decline continuously with age and polyamine (spermidine or high-polyamine diet) supplementation increases life span in model organisms. Polyamines have also been involved in stress resistance. On the other hand, polyamines are increased in cancer cells and are a target for potential chemotherapeutic agents. In this review, we bring together these various results and draw a picture of the state of our knowledge on the roles of polyamines in aging, stress and diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interest to declare.
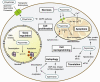
Figures


Similar articles
-
The old and new biochemistry of polyamines.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018 Sep;1862(9):2053-2068. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.06.004. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018. PMID: 29890242 Review.
-
Alzheimer's disease as a chronic maladaptive polyamine stress response.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Apr 3;13(7):10770-10795. doi: 10.18632/aging.202928. Epub 2021 Apr 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33811757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyamine Homeostasis in Development and Disease.Med Sci (Basel). 2021 May 13;9(2):28. doi: 10.3390/medsci9020028. Med Sci (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34068137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of polyamines in microorganisms.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Oct 27;33(11):204. doi: 10.1007/s11274-017-2370-y. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 29080149 Review.
-
Polyamines: essential factors for growth and survival.Planta. 2008 Aug;228(3):367-81. doi: 10.1007/s00425-008-0772-7. Epub 2008 Jul 2. Planta. 2008. PMID: 18594857 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of pepper extract with high polyamine levels; inhibition of ERK/MAPK pathway in mice.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 9;33(3):677-687. doi: 10.1007/s10068-023-01333-x. eCollection 2024 Feb. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38274190 Free PMC article.
-
Hypusinated eIF5A Promotes Ribosomal Frameshifting during Decoding of ODC Antizyme mRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 26;23(21):12972. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112972. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361762 Free PMC article.
-
The regulation of the sulfur amino acid biosynthetic pathway in Cryptococcus neoformans: the relationship of Cys3, Calcineurin, and Gpp2 phosphatases.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 15;9(1):11923. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48433-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31417135 Free PMC article.
-
The Involvement of Polyamines Catabolism in the Crosstalk between Neurons and Astrocytes in Neurodegeneration.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 21;10(7):1756. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071756. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35885061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of polyamines during the lifespan of plants: from development to stress.Planta. 2014 Jul;240(1):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2055-9. Planta. 2014. PMID: 24659098 Review.
References
-
- Bachrach U. The early history of polyamine research. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2010;48:490–495. - PubMed
-
- Hussain SS, Ali M, Ahmad M, Siddique KHM. Polyamines: Natural and engineered abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants. Biotechnol Adv. 2011 DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.01.003. - PubMed
-
- Wallace HM, Fraser AV. Inhibitors of polyamine metabolism: Review article. Amino acids. 2004;26:353–365. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberg T, Knauer H, Schauer A, Fussi H, Büttner S, Carmona-Gutierrez D, Ruckenstuhl C, Fahrenkrog B, Deszcz L, Hartl R, Weiskopf D, Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Herker E, et al. Induction of autophagy by spermidine promotes longevity. Nature Cell Biol. 2009;11:1305–1314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

