Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor enhances human islet posttransplantation survival
- PMID: 21869742
- PMCID: PMC3684966
- DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e31822bc95a
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor enhances human islet posttransplantation survival
Abstract
Background: Development of pretransplantation islet culture strategies that preserve or enhance β-cell viability would eliminate the requirement for the large numbers of islets needed to restore insulin independence in type 1 diabetes patients. We investigated whether glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) could improve human islet survival and posttransplantation function in diabetic mice.
Methods: Human islets were cultured in medium supplemented with or without GDNF (100 ng/mL) and in vitro islet survival and function assessed by analyzing β-cell apoptosis and glucose stimulated insulin release. In vivo effects of GDNF were assessed in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nude mice transplanted under the kidney capsule with 2000 islet equivalents of human islets precultured in medium supplemented with or without GDNF.
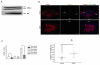
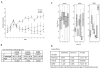
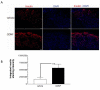
Results: In vitro, human islets cultured for 2 to 10 days in medium supplemented with GDNF showed lower β-cell death, increased Akt phosphorylation, and higher glucose-induced insulin secretion than islets cultured in vehicle. Human islets precultured in medium supplemented with GDNF restored more diabetic mice to normoglycemia and for a longer period after transplantation than islets cultured in vehicle.
Conclusions: Our study shows that GDNF has beneficial effects on human islet survival and could be used to improve islet posttransplantation survival.
Figures

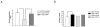

References
-
- Shapiro AMJ, Lakey JRT, Ryan EA, et al. Islet Transplantation in Seven Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Using a Glucocorticoid-Free Immunosuppressive Regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(4):230. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, et al. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(13):1318. - PubMed
-
- Hering BJ, Kandaswamy R, Ansite JD, et al. Single-Donor, Marginal-Dose Islet Transplantation in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes. JAMA. 2005;293(7):830. - PubMed
-
- Froud T, Ricordi C, Baidal DA, et al. Islet Transplantation in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Using Cultured Islets and Steroid-Free Immunosuppression: Miami Experience. American Journal of Transplantation. 2005;5(8):2037. - PubMed
-
- O'Connell PJ, Hawthorne WJ, Holmes-Walker DJ, et al. Clinical islet transplantation in type 1 diabetes mellitus: results of Australia's first trial. Med J Aust. 2006;184(5):221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

