L-selectin and SDF-1 enhance the migration of mouse and human cardiac mesoangioblasts
- PMID: 21869829
- PMCID: PMC3263491
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2011.110
L-selectin and SDF-1 enhance the migration of mouse and human cardiac mesoangioblasts
Abstract
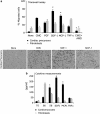
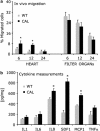
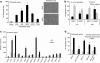
Efficient delivery of stem cells to heart regions is still a major problem for cell therapy. Here, we report experiments aimed to improve migration of mouse and human cardiac mesoangioblasts to the damaged heart. Cardiac mesoangioblasts were induced to transmigrate through the endothelium by factors released by cardiomyocytes or cytokines, among which stromal-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) was the most potent. Cardiac mesoangioblasts were also delivered into the left ventricular (LV) chamber of mice after coronary artery ligation (CAL), and their in vivo homing to the damaged heart was found to be quite modest. Pretreatment of cardiac mesoangioblasts with SDF-1 or transient expression of L-selectin induced a two- to three-fold increase in their transmigration and homing to the damaged heart. Therefore, combined pretreatment with SDF-1 and L-selectin generated modified cardiac mesoangioblasts, 50% of which, after injection into the LV chamber of mice early after CAL, home directly to the damaged free wall of the heart. Finally, modified mouse cardiac mesoangioblasts, injected into the LV chamber regenerate a larger surface of the ventricle in long-term experiments in comparison with their control counterparts. This study defines the requirements for efficient homing of cardiac mesoangioblasts to the damaged heart and offers a new potent tool to optimize efficiency of future cell therapy protocols for cardiovascular diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Butcher E. Leukocyte-endothelial cell recognition: three (or more) steps to specificity and diversity. Cell. 1991;67:1033–1036. - PubMed
-
- Fu S, Liesveld J. Mobilization of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood Rev. 2000;14:205–218. - PubMed
-
- Grabovsky V, Feigelson S, Chen C, Bleijs D, Peled A, Cinamon G, et al. Subsecond induction of alpha4 integrin clustering by immobilized chemokines stimulates leukocyte tethering and rolling on endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 under flow conditions. J Exp Med. 2000;192:495–506. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peled A, Kollet O, Ponomaryov T, Petit I, Franitza S, Grabovsky V, et al. The chemokine SDF-1 activates the integrins LFA-1, VLA-4, and VLA-5 on immature human CD34(+) cells: role in transendothelial/stromal migration and engraftment of NOD/SCID mice. Blood. 2000;95:3289–3296. - PubMed
-
- Springer T. Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell. 1994;76:301–314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

