Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α regulates Fas-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis during osteoarthritic cartilage destruction
- PMID: 21869830
- PMCID: PMC3278727
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2011.111
Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α regulates Fas-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis during osteoarthritic cartilage destruction
Abstract
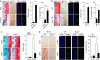
Apoptosis of articular chondrocytes is associated with the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis (OA). Recently, we demonstrated that hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-2α, encoded by Epas1, causes OA cartilage destruction by regulating the expression of various matrix-degrading enzymes. Here, we investigated the involvement of HIF-2α in chondrocyte apoptosis and OA cartilage destruction. HIF-2α levels in human and mouse OA chondrocytes were markedly elevated in association with increased apoptosis of articular chondrocytes. Overexpression or knockdown of HIF-2α alone did not cause chondrocyte apoptosis. However, HIF-2α expression markedly increased chondrocyte apoptosis in the presence of an agonistic anti-Fas (CD95) antibody. HIF-2α enhanced Fas expression and potentiated downstream signaling pathways, increasing the activity of initiator and executioner caspases. Overexpression of HIF-2α in mouse cartilage tissue, either by intra-articular injection of Epas1 adenovirus (Ad-Epas1) or in the context of chondrocyte-specific Epas1 transgenic mice, increased chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage destruction. In contrast, chondrocyte-specific knockout of Epas1 in mice suppressed DMM (destabilization of the medial meniscus)-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and inhibited OA cartilage destruction. Moreover, Fas-deficient mice exhibited diminished chondrocyte apoptosis and OA cartilage destruction in response to Ad-Epas1 injection or DMM surgery. Taken together, our results demonstrate that HIF-2α potentiates Fas-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis, which is associated with OA cartilage destruction.
Figures

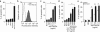


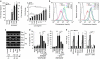


References
-
- Goldring MB, Goldring SR. Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213:626–634. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto M, Nakasa T, Hikata T, Asahara H. Molecular network of cartilage homeostasis and osteoarthritis. Med Res Rev. 2008;28:464–481. - PubMed
-
- Kühn K, D'Lima DD, Hashimoto S, Lotz M. Cell death in cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Kim HA, Blanco FJ. Cell death and apoptosis in osteoarthritic cartilage. Curr Drug Targets. 2007;8:333–345. - PubMed
-
- Blanco FJ, Guitian R, Vazquez-Martul E, de Toro FJ, Galdo F. Osteoarthritis chondrocytes die by apoptosis. A possible pathway for osteoarthritis pathology. Arthritis Rheum. 1998;41:284–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

