Acquired activated protein C resistance, thrombophilia and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a study performed in an Irish cohort of pregnant women
- PMID: 21869933
- PMCID: PMC3157763
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/232840
Acquired activated protein C resistance, thrombophilia and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a study performed in an Irish cohort of pregnant women
Abstract
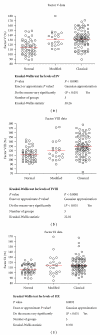
The combination of thrombophilia and pregnancy increases the risk of thrombosis and the potential for adverse outcomes during pregnancy. The most significant common inherited risk factor for thrombophilia is activated protein C resistance (APCR), a poor anticoagulant response of APC in haemostasis, which is mainly caused by an inherited single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), factor V G1691A (FV Leiden) (FVL), referred as inherited APCR. Changes in the levels of coagulation factors: FV, FVIII, and FIX, and anticoagulant factors: protein S (PS) and protein C (PC) can alter APC function causing acquired APCR. Prothrombin G20210A and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) C677T are prothrombotic SNPs which in association with APCR can also increase the risk of thrombosis amongst Caucasians. In this study, a correlation between an acquired APCR phenotype and increased levels of factors V, VIII, and IX was demonstrated. Thrombophilic mutations amongst our acquired APCR pregnant women cohort are relatively common but do not appear to exert a severe undue adverse effect on pregnancy.
Figures
References
-
- Gwyneth L, editor. Reports on Public Health and Medical Subjects 1994–1996. London, UK: Department of Health United Kingdom; 1998. Report on confidential enquiries into maternal deaths.
-
- Knijff SCM, editor. Summary of Contraindications to Oral Contraceptives. New York, NY, USA: Parthenon Publishing Group; 2000.
-
- Martinelli I. Risk factors in venous thromboembolism. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86:395–403. - PubMed
-
- Kalafatis M, Bertina RM, Rand MD, Mann KG. Characterization of the molecular defect in factor V(R506Q) Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1995;270(8):4053–4057. - PubMed
-
- Axelsson F, Rosen S. APC Resistance. Chromogenix AB; (Product Monograph 1997). version 2.1 1997.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources