Nanocarriers for nitric oxide delivery
- PMID: 21869934
- PMCID: PMC3159988
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/936438
Nanocarriers for nitric oxide delivery
Abstract
Nitric oxide (NO) is a promising pharmaceutical agent that has vasodilative, antibacterial, and tumoricidal effects. To study the complex and wide-ranging roles of NO and to facilitate its therapeutic use, a great number of synthetic compounds (e.g., nitrosothiols, nitrosohydroxyamines, N-diazeniumdiolates, and nitrosyl metal complexes) have been developed to chemically stabilize and release NO in a controlled manner. Although NO is currently being exploited in many biomedical applications, its use is limited by several factors, including a short half-life, instability during storage, and potential toxicity. Additionally, efficient methods of both localized and systemic in vivo delivery and dose control are needed. One strategy for addressing these limitations and thus increasing the utility of NO donors is based on nanotechnology.
Figures
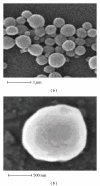

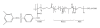
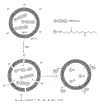
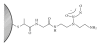

References
-
- Waldman SA, Rapoport RM, Ginsburg R, Murad F. Desensitization to nitroglycerin in vascular smooth muscle from rat and human. Biochemical Pharmacology. 1986;35(20):3525–3531. - PubMed
-
- Butler AR. The biological roles of nitric oxide. Chemistry and Industry. 1995;20:828–830.
-
- Garthwaite J, Boulton CL. Nitric oxide signaling in the central nervous system. Annual Review of Physiology. 1995;57:683–706. - PubMed
-
- Ignarro LJ, Cirino G, Casini A, Napoli C. Nitric oxide as a signaling molecule in the vascular system: an overview. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology. 1999;34(6):879–886. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

