Distinctive disruption patterns of white matter tracts in Alzheimer's disease with full diffusion tensor characterization
- PMID: 21872362
- PMCID: PMC3227739
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.06.027
Distinctive disruption patterns of white matter tracts in Alzheimer's disease with full diffusion tensor characterization
Abstract
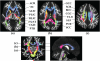
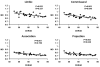
To characterize the white matter structural changes at the tract level and tract group level, comprehensive analysis with 4 metrics derived from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), axial diffusivity (AxD) and radial diffusivity (RD), was conducted. Tract groups, namely limbic, commissural, association, and projection tracts, include white matter tracts of similar functions. Diffusion tensor imaging data were acquired from 61 subjects (26 Alzheimer's disease [AD], 11 subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment [aMCI], and 24 age-matched controls). An atlas-based approach was used to survey 30 major cerebral white matter tracts with the measurements of FA, MD, AxD, and RD. Regional cortical atrophy and cognitive functions of AD patients were also measured to correlate with the structural changes of white matter. Synchronized structural changes of cingulum bundle and fornix, both of which are part of limbic tract group, were revealed. Widespread yet distinctive structural changes were found in limbic, commissural, association, and projection tract groups between control and AD subjects. Specifically, FA, MD, and RD of limbic tracts, FA, MD, AxD, and RD of commissural tracts, MD, AxD, and RD of association tracts, and MD and AxD of projection tracts are significantly different between AD patients and control subjects. In contrast, the comparison between aMCI and control subjects shows disruption only in the limbic and commissural tract groups of aMCI subjects. MD values of all tract groups of AD patients are significantly correlated to cognitive functions. Difference between AD and control and that between aMCI and control indicates a progression pattern of white matter disruption from limbic and commissural tract group to other tract groups. High correlation between FA, MD, and RD measurements from limbic tracts and cortical atrophy suggests the disruption of the limbic tract group is caused by the neuronal damage.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
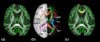
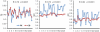


References
-
- Acosta-Cabronero J, Williams GB, Pengas G, Nestor PJ. Absolute diffusivities define the landscape of white matter degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2010;133:529–539. - PubMed
-
- Alexander AL, Hasan KM, Lazar M, Tsuruda JS, Parker DL. Analysis of partial volume effects in diffusion-tensor MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2001;45:770–780. - PubMed
-
- Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control. 1974;19:716–723.
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Voxel-Based Morphometry--The Methods. NeuroImage. 2000;11:805–821. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Why Voxel-Based Morphometry Should Be Used. NeuroImage. 2001;14:1238–1243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

