Analysis of the interaction of the Eg5 Loop5 with the nucleotide site
- PMID: 21872609
- PMCID: PMC3191284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2011.08.017
Analysis of the interaction of the Eg5 Loop5 with the nucleotide site
Abstract
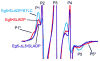
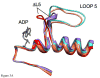
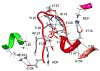
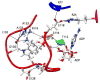
Loop 5 (L5) is a conserved loop that projects from the α2-helix adjacent to the nucleotide site of all kinesin-family motors. L5 is critical to the function of the mitotic kinesin-5 family motors and is the binding site for several kinesin-5 inhibitors that are currently in clinical trials. Its conformational dynamics and its role in motor function are not fully understood. Our previous work using EPR spectroscopy suggested that L5 alters the nucleotide pocket conformation of the kinesin-5 motor Eg5 (Larson et al., 2010). EPR spectra of a spin-labeled nucleotide analog bound at the nucleotide site of Eg5 display a highly immobilized component that is absent if L5 is shortened or if the inhibitor STLC is added (Larson et al., 2010), which X-ray structures suggest stabilizes an L5 conformation pointing away from the nucleotide site. These data, coupled with the proximity of L5 to the nucleotide site suggest L5 could interact with a bound nucleotide, modulating function. Here we use molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of Eg5 to explore the interaction of L5 with the nucleotide site in greater detail. We performed MD simulations in which the L5-domain of the Eg5·ADP X-ray structure was manually deformed via backbone bond rotations. The L5-domain of Eg5 was sufficiently lengthy that portions of L5 could be located in proximity to bound ADP. The MD simulations evolved to thermodynamically stable structures at 300 K showing that L5 can interact directly with bound nucleotide with significant impingement on the ribose hydroxyls, consistent with the EPR spectroscopy results. Taken together, these data provide support for the hypothesis that L5 modulates Eg5 function via interaction with the nucleotide-binding site.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
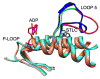








References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

