Transcription factor AP4 modulates reversible and epigenetic silencing of the Cd4 gene
- PMID: 21873191
- PMCID: PMC3169121
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1112293108
Transcription factor AP4 modulates reversible and epigenetic silencing of the Cd4 gene
Abstract
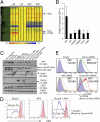
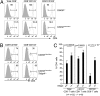
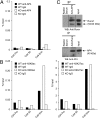
CD4 coreceptor expression is negatively regulated through activity of the Cd4 silencer in CD4(-)CD8(-) double-negative (DN) thymocytes and CD8(+) cytotoxic lineage T cells. Whereas Cd4 silencing is reversed during transition from DN to CD4(+)CD8(+) double-positive stages, it is maintained through heritable epigenetic processes following its establishment in mature CD8(+) T cells. We previously demonstrated that the Runx family of transcription factors is required for Cd4 silencing both in DN thymocytes and CD8(+) T cells. However, additional factors that cooperate with Runx proteins in the process of Cd4 silencing remain unknown. To identify collaborating factors, we used microarray and RNAi-based approaches and found the basic helix-loop-helix ZIP transcription factor AP4 to have an important role in Cd4 regulation. AP4 interacts with Runx1 in cells in which Cd4 is silenced, and is required for Cd4 silencing in immature DN thymocytes through binding to the proximal enhancer. Furthermore, although AP4-deficient CD8(+) T cells appeared to normally down-regulate CD4 expression, AP4 deficiency significantly increased the frequency of CD4-expressing effector/memory CD8(+) T cells in mice harboring point mutations in the Cd4 silencer. Our results suggest that AP4 contributes to Cd4 silencing both in DN and CD8(+) T cells by enforcing checkpoints for appropriate timing of CD4 expression and its epigenetic silencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kioussis D, Ellmeier W. Chromatin and CD4, CD8A and CD8B gene expression during thymic differentiation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:909–919. - PubMed
-
- Taniuchi I, Sunshine MJ, Festenstein R, Littman DR. Evidence for distinct CD4 silencer functions at different stages of thymocyte differentiation. Mol Cell. 2002;10:1083–1096. - PubMed
-
- Zou YR, et al. Epigenetic silencing of CD4 in T cells committed to the cytotoxic lineage. Nat Genet. 2001;29:332–336. - PubMed
-
- Taniuchi I, et al. Differential requirements for Runx proteins in CD4 repression and epigenetic silencing during T lymphocyte development. Cell. 2002;111:621–633. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

