Mobilization of natural killer cells inhibits development of collagen-induced arthritis
- PMID: 21873193
- PMCID: PMC3167502
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1112188108
Mobilization of natural killer cells inhibits development of collagen-induced arthritis
Abstract
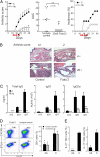
Although natural killer (NK) cells have been implicated in regulating immune responses, their ability to modulate disease development in autoimmune arthritis has not been analyzed. Here we investigate the contribution of NK cells to regulating collagen-induced arthritis, a well-characterized preclinical model of human rheumatoid arthritis. We find that the disease is induced by the combined action of two CD4(+) T helper (T(H)) subsets: follicular T(H) cells and T(H)17 cells. Both CD4(+) T(H) subsets are highly susceptible to lysis by NK cells after activation. Administration of antibody that activates NK cells through blockade of its inhibitory CD94/NKG2A receptor allows enhanced elimination of pathogenic follicular T(H) and T(H)17 cells and arrest of disease progression. These results suggest that antibody-dependent enhancement of NK activity may yield effective, previously undescribed therapeutic approaches to this autoimmune disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

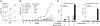


Comment in
-
Experimental arthritis: Mobilizing killer cells to combat CIA.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011 Oct 18;7(11):622. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2011.147. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 22009332 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cho YG, Cho ML, Min SY, Kim HY. Type II collagen autoimmunity in a mouse model of human rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2007;7:65–70. - PubMed
-
- Asquith DL, Miller AM, McInnes IB, Liew FY. Animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 2009;39:2040–2044. - PubMed
-
- Bevaart L, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Tak PP. Evaluation of therapeutic targets in animal models of arthritis: How does it relate to rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2192–2205. - PubMed
-
- Leipe J, et al. Role of Th17 cells in human autoimmune arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2876–2885. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

