Topology of human apolipoprotein E3 uniquely regulates its diverse biological functions
- PMID: 21873229
- PMCID: PMC3169138
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1106420108
Topology of human apolipoprotein E3 uniquely regulates its diverse biological functions
Abstract
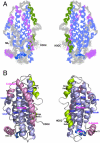
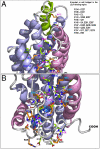
Human apolipoprotein E (apoE) is one of the major determinants in lipid transport, playing a critical role in atherosclerosis and other diseases. Binding to lipid and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG) induces apoE to adopt active conformations for binding to low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) family. ApoE also interacts with beta amyloid peptide, manifests critical isoform-specific effects on Alzheimer's disease. Despite the importance of apoE in these major human diseases, the fundamental questions of how apoE adjusts its structure upon binding to regulate its diverse functions remain unsolved. We report the NMR structure of apoE3, displaying a unique topology of three structural domains. The C-terminal domain presents a large exposed hydrophobic surface that likely initiates interactions with lipids, HSPG, and beta amyloid peptides. The unique topology precisely regulates apoE tertiary structure to permit only one possible conformational adaptation upon binding and provides a double security in preventing lipid-free and partially-lipidated apoE from premature binding to apoE receptors during receptor biogenesis. This topology further ensures the optimal receptor-binding activity by the fully lipidated apoE during lipoprotein transport in circulation and in the brain. These findings provide a structural framework for understanding the structural basis of the diverse functions of this important protein in human diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Weisgraber KH. Apolipoprotein E: structure-function relationships. Adv Protein Chem. 1994;45:249–302. - PubMed
-
- Mahley RW, Ji ZS. Remnant lipoprotein metabolism: key pathways involving cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans and apolipoprotein E. J Lipid Res. 1999;40:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Luc G, et al. Impact of apolipoprotein E polymorphism on lipoproteins and risk of myocardial infarction. The ECTIM Study. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994;14:1412–1419. - PubMed
-
- Mahley RW, Rall SC Jr, editors. The Metabolic and Molecular Base of Inherited Disease. 8 Ed. New York: (McGraw-Hill); 2001. pp. 2835–2862.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

