Antibodies recognising sulfated carbohydrates are prevalent in systemic sclerosis and associated with pulmonary vascular disease
- PMID: 21873333
- PMCID: PMC3409247
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2011.153130
Antibodies recognising sulfated carbohydrates are prevalent in systemic sclerosis and associated with pulmonary vascular disease
Abstract
Background: Glycosylation represents an important modification that regulates biological processes in tissues relevant for disease pathogenesis in systemic sclerosis (SSc), including the endothelium and extracellular matrix. Whether patients with SSc develop antibodies to carbohydrates is not known.
Objectives: To determine the prevalence and clinical phenotype associated with serum IgG antibodies recognising distinct glycans in patients with SSc.
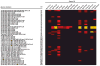
Methods: Pooled serum samples from patients with SSc and controls were screened for the presence of specific anticarbohydrate antibodies using a novel array containing over 300 glycans. Antibody titres to 4-sulfated N-acetyl-lactosamine (4S-LacNAc, (4OSO3)Galβ1-4GlcNAc) were determined in 181 individual serum samples from patients with SSc by ELISA and associated with disease phenotype.
Results: 4S-LacNAc was identified as a target in pooled SSc serum. Anti-4S-LAcNAc antibodies were detected in 27/181 patients with SSc (14.9%) compared with 1/40 healthy controls (2.5%). Sulfation at position C4 of galactose (4S-LacNAc) was found to be critical for immunogenicity. Anti-4S-LacNAc antibody-positive patients with SSc had a higher prevalence of pulmonary hypertension by echocardiography than anti-4S-LacNAc-negative patients (15/27 (55.7%) vs 49/154 (31.8%), p=0.02) with an OR of 2.6 (95% CI 1.1 to 6.3). Anti-4S-LacNAc-positive patients accounted for 23.4% of all patients with pulmonary hypertension.
Conclusion: Serum from patients with SSc contains IgG antibodies targeting distinct sulfated carbohydrates. The presence of anti-4S-LacNAc antibodies is associated with a high prevalence of pulmonary hypertension. These results suggest that specific post-translational carbohydrate modifications may act as important immunogens in SSc and may contribute to disease pathogenesis.
Figures
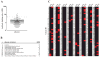
 ABR > 2 SD from mean).
ABR > 2 SD from mean).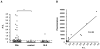
 ) low positive, (
) low positive, (
 ) medium positive, (
) medium positive, (
 ) high positive (as defined in Materials and Methods). (*) denotes anti-4S-LacNAc positive patients as determined by ELISA.
) high positive (as defined in Materials and Methods). (*) denotes anti-4S-LacNAc positive patients as determined by ELISA.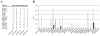
 ) 6S-LacNAc). 1 of the 27 anti-4S-LacNAc positive sera was not available for further testing.
) 6S-LacNAc). 1 of the 27 anti-4S-LacNAc positive sera was not available for further testing.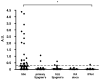
References
-
- Wigley FM. Vascular disease in scleroderma. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2009;36:150–175. - PubMed
-
- Harris ML, Rosen A. Autoimmunity in scleroderma: the origin, pathogenetic role, and clinical significance of autoantibodies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;15:778–784. - PubMed
-
- Mihai C, Tervaert JW. Anti-endothelial cell antibodies in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:319–324. - PubMed
-
- Chizzolini C, Raschi E, Rezzonico R, et al. Autoantibodies to fibroblasts induce a proadhesive and proinflammatory fibroblast phenotype in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:1602–1613. - PubMed
-
- Baroni SS, Santillo M, Bevilacqua F, et al. Stimulatory autoantibodies to the PDGF receptor in systemic sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2667–2676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

