Cutting edge: accelerated autoimmune diabetes in the absence of LAG-3
- PMID: 21873518
- PMCID: PMC3178660
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100714
Cutting edge: accelerated autoimmune diabetes in the absence of LAG-3
Abstract
Lymphocyte activation gene-3 (LAG-3; CD223) is a CD4 homolog that is required for maximal regulatory T cell function and for the control of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell homeostasis. Lag3(-)(/)(-) NOD mice developed substantially accelerated diabetes with 100% incidence. Adoptive transfer experiments revealed that LAG-3 was primarily responsible for limiting the pathogenic potential of CD4(+) T cells and, to a lesser extent, CD8(+) T cells. Lag3(-)(/)(-) mice exhibited accelerated, invasive insulitis, corresponding to increased CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell islet infiltration and intraislet proliferation. The frequencies of islet Ag-reactive chromogranin A-specific CD4(+) T cells and islet specific glucose-6-phosphatase-specific CD8(+) T cells were significantly increased in the islets of Lag3(-)(/)(-) mice, suggesting an early expansion of pathogenic clones that is normally restrained by LAG-3. We conclude that LAG-3 is necessary for regulating CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell function during autoimmune diabetes, and thus may contribute to limiting autoimmunity in disease-prone environments.
Figures
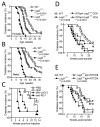

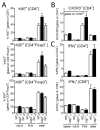

References
-
- Lehuen A, Diana J, Zaccone P, Cooke A. Immune cell crosstalk in type 1 diabetes. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:501–513. - PubMed
-
- Workman CJ, Cauley LS, Kim IJ, Blackman MA, Woodland DL, Vignali DA. Lymphocyte activation gene-3 (CD223) regulates the size of the expanding T cell population following antigen activation in vivo. J Immunol. 2004;172:5450–5455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

