An acquired defect in IgG-dependent phagocytosis explains the impairment in antibody-mediated cellular depletion in Lupus
- PMID: 21873531
- PMCID: PMC3178685
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101629
An acquired defect in IgG-dependent phagocytosis explains the impairment in antibody-mediated cellular depletion in Lupus
Abstract
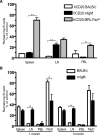
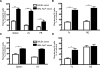
B cells play important roles in autoimmune diseases ranging from multiple sclerosis to rheumatoid arthritis. B cells have also long been considered central players in systemic lupus erythematosus. However, anti-CD20-mediated B cell depletion was not effective in two clinical lupus studies, whereas anti-B lymphocyte stimulator, which inhibits B cell survival, was effective. Others and we previously found that anti-CD20-based depletion was surprisingly ineffective in tissues of lupus-prone mice, but that persistent high doses eventually led to depletion and ameliorated lupus. Lupus patients might also have incomplete depletion, as suggested in several studies, and which could have led to therapeutic failure. In this study, we investigated the mechanism of resistance to Ab-mediated cellular depletion in murine lupus. B cells from lupus-prone mice were easily depleted when transferred into normal environments or in lupus-prone mice that lacked serum Ig. Serum from lupus-prone mice transferred depletion resistance, with the active component being IgG. Because depletion is FcγR-dependent, we assayed macrophages and neutrophils exposed to lupus mouse serum, showing that they are impaired in IgG-mediated phagocytosis. We conclude that depletion resistance is an acquired, reversible phagocytic defect depending on exposure to lupus serum IgG. These results have implications for optimizing and monitoring cellular depletion therapy.
Figures
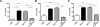


References
-
- Martin F, Chan AC. B cell immunobiology in disease: evolving concepts from the clinic. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2006;24:467–496. - PubMed
-
- Browning JL. B cells move to centre stage: novel opportunities for autoimmune disease treatment. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:564–576. - PubMed
-
- Chan OT, Madaio MP, Shlomchik MJ. B cells are required for lupus nephritis in the polygenic, Fas-intact MRL model of systemic autoimmunity. J Immunol. 1999;163:3592–3596. - PubMed
-
- Looney RJ. B cells as a therapeutic target in autoimmune diseases other than rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2005;44(Suppl 2):ii13–ii17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

